Doped CdSe quantum dots capture more energy from light
Los Alamos National Lab team discover new way to capture energy from light-generated, 'hot' electrons
Los Alamos National Laboratory scientists have synthesised magnetically-doped quantum dots that capture the kinetic energy of electrons created by ultraviolet light before it's wasted as heat.
"This discovery can potentially enable novel, highly-efficient solar cells, light detectors, photocathodes and light-driven chemical reactions," said Victor Klimov, lead researcher on the Laboratory's quantum dot project.
In standard solar cells, a large amount of sunlight energy is wasted as heat. This waste occurs due to the lack of effective approaches for capturing kinetic energy of 'hot' electrons generated by photons in the green to ultraviolet portion of the sun's light spectrum. The problem is that hot electrons lose their energy very quickly due to interactions with crystal lattice that the devices are made of, leading to vibrations known as phonons. This process typically occurs in a few picoseconds (trillionths of a second).
Previous efforts to capture hot-carrier energy have exploited the transfer of kinetic energy from the energetic hot electron to an immobile, low-energy electron exciting it to a current-conducting state. This effect, known as carrier multiplication, doubles the number of electrons contributing to the photocurrent which can be used for boosting the performance of solar cells. In most conventional materials, however, the energy losses to phonons outpace the energy gains of carrier multiplication.
In their study published in Nature Nanotechnology, researchers demonstrate that incorporating magnetic ions into quantum dots can greatly enhance useful, energy-producing interactions so as they become faster than wasteful phonon scattering.
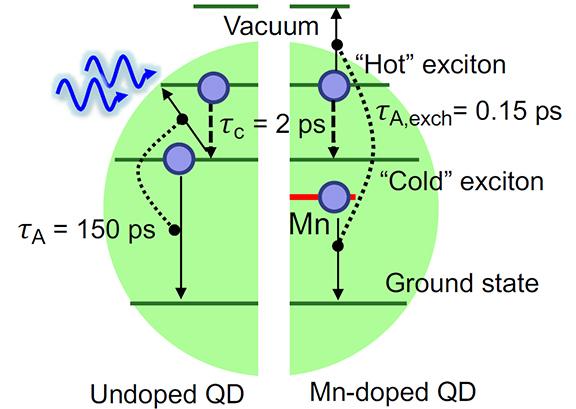
To implement these ideas, the researchers prepared manganese-doped quantum dots based on CdSe. "The photon absorbed by the CdSe quantum dot creates an electron-hole pair, or an exciton," said Klimov."This exciton is quickly trapped by the dopant creating an excited state that stores energy much like a compressed spring. When the second photon is absorbed by the quantum dot, the stored energy is released and transferred to the newly created exciton promoting it to a higher-energy state. The energy release by the manganese ion is accompanied by the flip of its magnetic moment, known as spin. Hence this process is termed spin-exchange Auger energy transfer."
The right half of graphic (above) shows how doping with manganese speeds the capture of energy from a hot electron to 0.15 picoseconds, outpacing losses to phonons in the crystal lattice.
These paradigm-shifting findings open exciting opportunities for exploiting spin-exchange Auger processes in advanced schemes for boosting the performance of solar cells or driving unusual photochemical reactions. Interesting opportunities are also envisioned in areas of high-sensitivity, high-speed light detection and new types of light-driven electron sources.
The work was supported by the Solar Photochemistry Program of the Chemical Sciences, Biosciences and Geosciences Division, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Office of Science, US Department of Energy.
'Hot-Electron Dynamics in Quantum Dots Manipulated by Spin-Exchange Auger Interactions', by Rohan Singh et al; Nature Nanotechnology, 7th October 2019


































