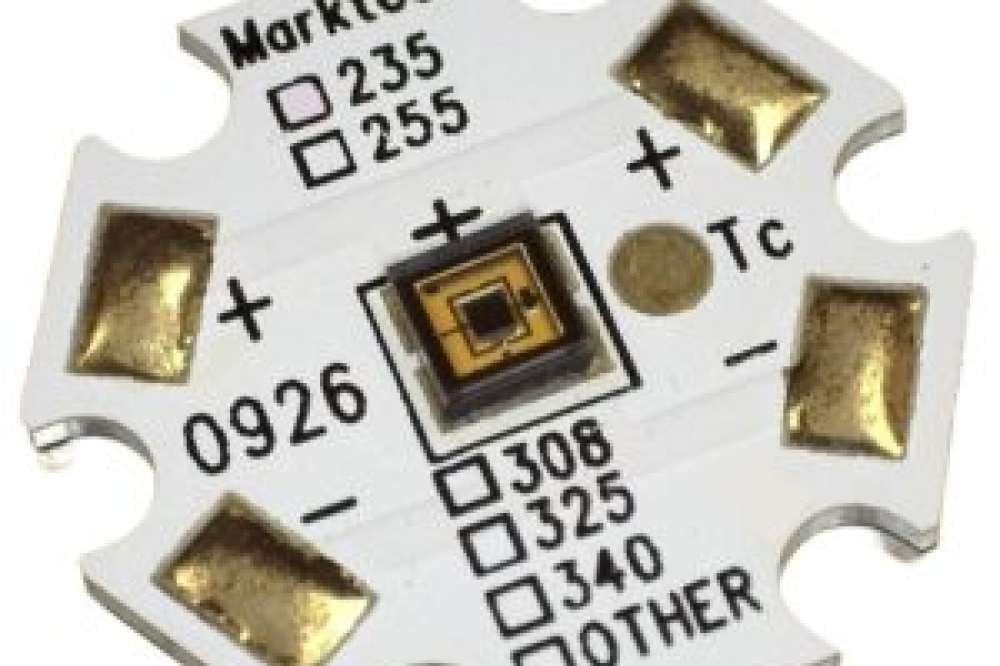
Mesa sidewall design improves HV DUV LEDs

A team from Wuhan University in China has developed a mesa sidewall engineering approach to enhance the optoelectronic performance of high-voltage deep DUV LEDs.
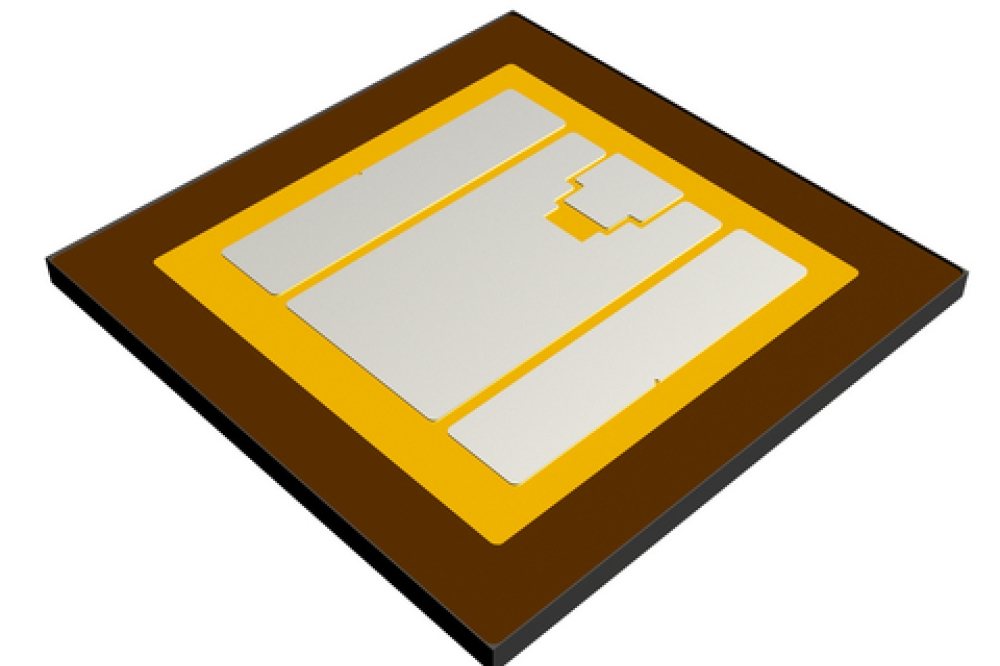
“We demonstrated that sub-mesas with an inclined angle of 46° combined with Al reflectors can maximise light extraction while mitigate self-heating effects. The high perimeter-to-area ratio of sub-mesas enables superior heat dissipation, leading to markedly lower efficiency droop in HV DUV LEDs,” explained Shengjun Zhou, who directed the research.
AlGaN-based DUV LEDs are critical for applications such as sterilisation, sensing, and water purification. However, their widespread adoption has been hindered by low light extraction efficiency (LEE) and severe efficiency droop at high injection currents, primarily caused by the self-heating effect and photon absorption losses.
To address these challenges, the team designed HV DUV LEDs with four sub-mesas, each featuring a precisely angled sidewall. Three-dimensional finite-difference time-domain simulations revealed that 46° sub-mesa sidewall with Al reflectors significantly improves the LEE of TM-polarised light.
Additionally, experimental validation showed that HV DUV LEDs with four sub-mesas exhibited an efficiency droop of 34.6 percent at 6.4 W input power—significantly lower than the 51.6 percent efficiency droop in single junction (SJ ) devices.
Electroluminescence spectra confirmed minimal wavelength redshift and narrower full-width half-maximum broadening in HV DUV LEDs, indicating effective heat dissipation.
The team says the study provides critical insights into mesa design of high-power DUV LEDs, paving the way for more reliable and efficient DUV light sources for industrial and environmental applications.
Reference
‘Design of high-voltage deep ultraviolet LED sub-mesas toward improved optoelectronic performance’ by Zhefu Liao et al.; Optics Letters 2024