Comparing MicroLED headlight technology
Two leading LED companies, Osram and Nichia, have developed dedicated microLED solutions for car headlights, enabling more than a 100-fold increase in resolution compared to current matrix LED systems based on discrete LEDs.
Yole Group has now released a reverse engineering and costing report, looking at these LED solutions for Adaptive Driving Beam (ADB). It says that while Osram and Nichia's car headlight solutions do the same job, the way they do it is different.
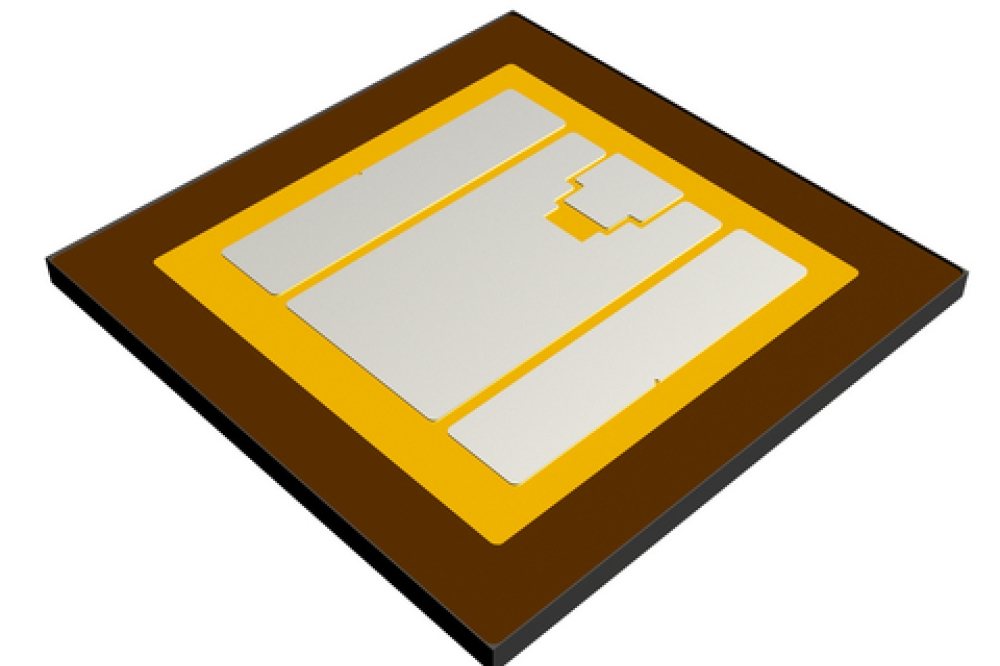
Osram's EVIYOS 2.0 technology uses a large GaN chiplet on which 25,600 microLEDs are patterned, whereas Nichia's µPLS is based on mass transfer technology. 16,384 microLEDs are manufactured on a sapphire/GaN substrate and assembled on an ASIC driver die.
Osram' has a large matrix LED die bonded to an ASIC driver die. Each microLED, with a 40 µm pitch, is directly driven by the ASIC die, allowing for the individual control of all 25,600 microLEDs. This pixel ADB solution has been integrated by Marelli into several cars, including the VW Touareg, Tiguan, Tayron (19 kpixels), Opel Grandland (25 kpixels), and Nio ET9 (25 kpixels).
According to Sylvain Hallereau, principal analyst, Global Semiconductors at Yole Group said, the driver die is designed and manufactured by Ams Osram at the Ams 200 foundry in Austria. The LED die is produced by Ams Osram at their LED foundry in Malaysia. "Additionally, based on our reverse engineering and cost analysis, we determined that the gold pad on the driver and the C2W bonding process are carried out by Ams Osram in Malaysia. We estimate that the packaging of the driver and LED die is also conducted by Ams Osram in Malaysia."
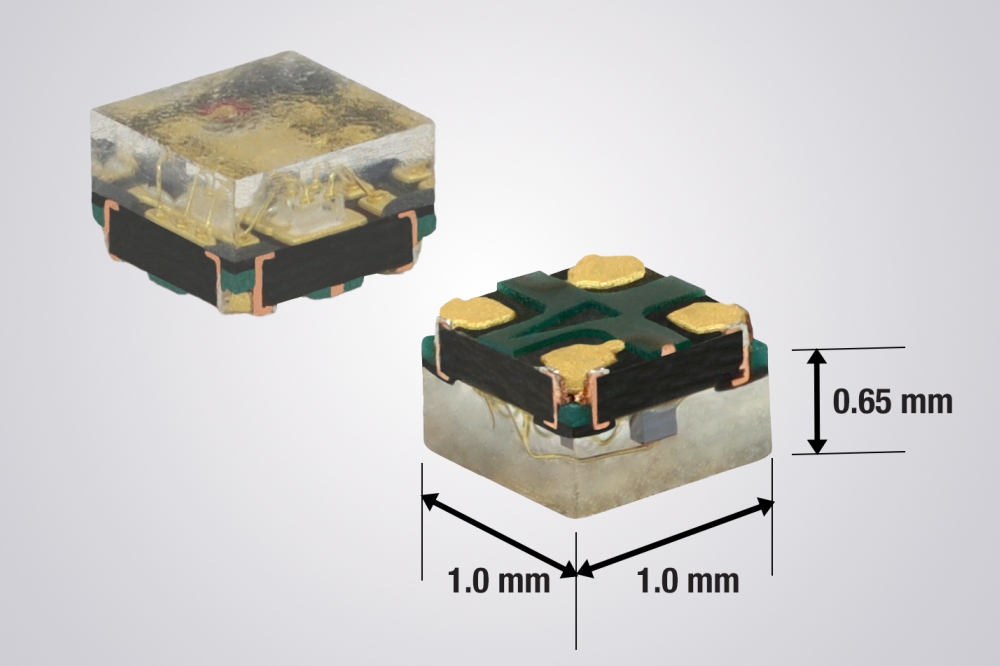
The second component analysed is the µPLS microLED from Nichia, featuring 16,384 pixels.
Pierrick Boulay, senior technology and market analyst, Automotive Semiconductors at Yole Group said: "Nichia’s technology differs significantly, as it is based on the mass transfer of 16,384 individual discrete microLEDs onto an ASIC die. Each microLED, with a 50 µm pitch, is directly driven by the ASIC die. This pixel ADB solution has been chosen by Forvia Hella for their high-end headlamps."
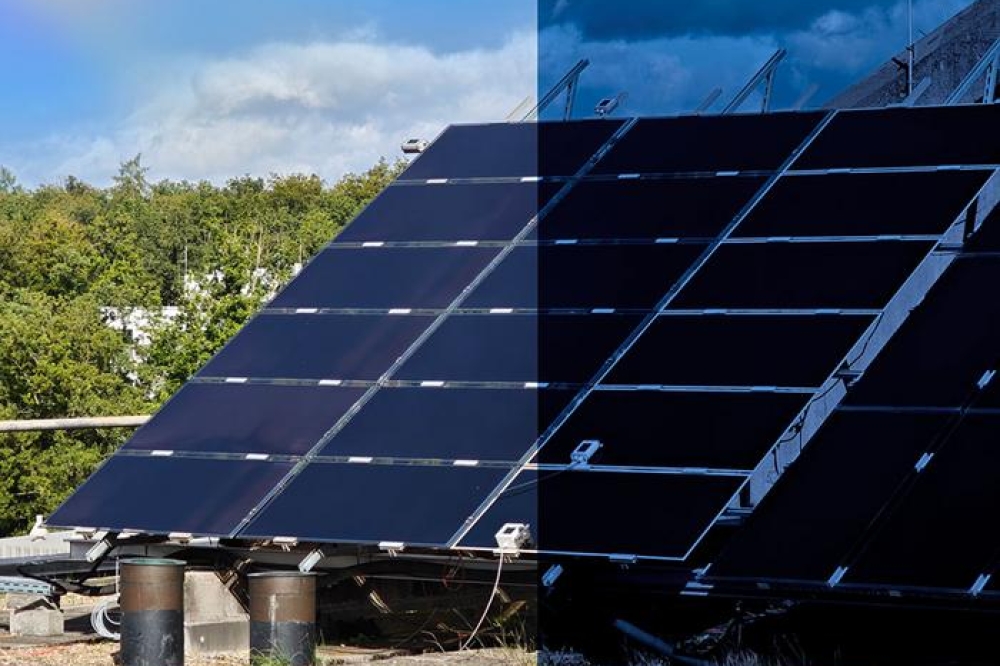
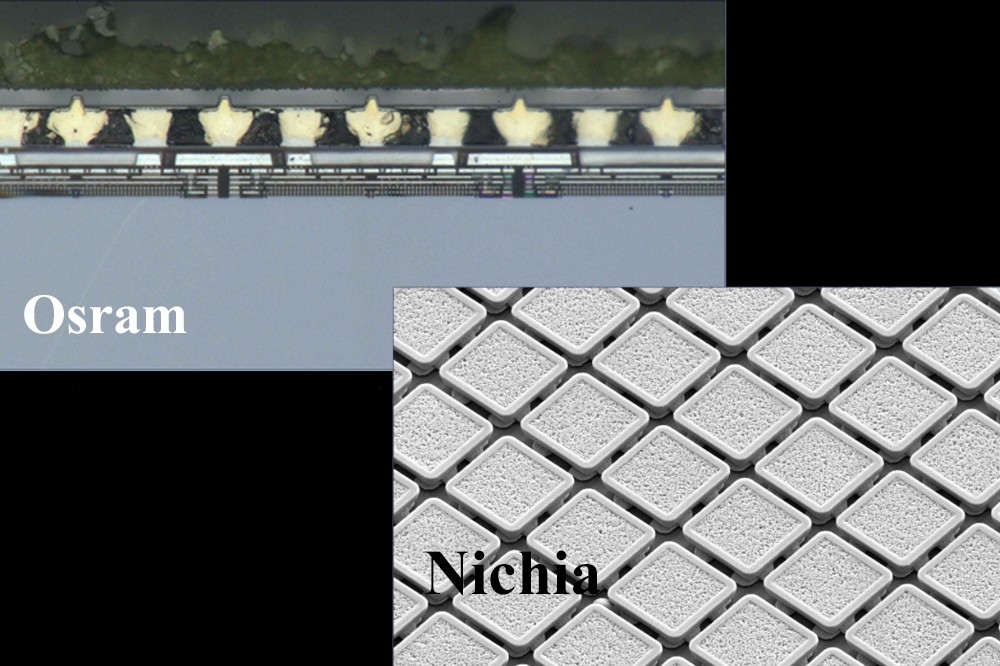
Pictured above: Osram technology (top left): Cross section of a matrix of micro LEDs manufactured on a large GaN chiplet and bonded on the drive ASIC. Each of the 25,600 microLEDs is individually driven by the ASIC
Nichia technology (bottom right): Matrix of microLEDs assembled by mass transfer on top of the driver ASIC. Each of the 16,384 microLEDs is individually driven by the ASIC