Artificial fog turns laser-diodes into useful lights
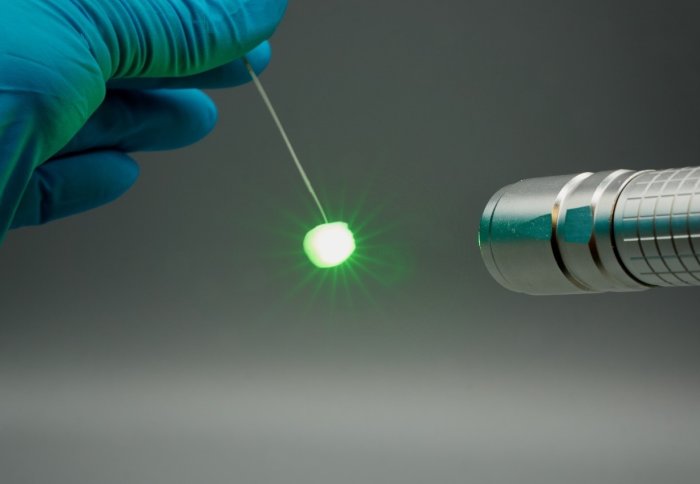
Scientists invent new way to create white light, by shining red, blue and green lasers into a diffuser made of 2D hBN
A team led by the EU Graphene Flagship with collaborators including the UK's Imperial College have invented a diffuser that scatters light from a laser diode, making it more useful in lighting larger areas.
The study, published in Nature Communications, also shows how the laser light can be tuned to different colours, including white, which has been difficult to achieve with lasers. Current uses of laser light are limited to a single colour and the light is very focused and narrow – for example in laser pointers, barcode scanners and DVD players.
Previously laser diode-based lights have created white light by shining a laser onto phosphor materials, but the process is not very efficient and can only create one colour of light.
The team invented a new way to create white light, by shining red, blue and green lasers into a diffuser made of 2D hexagonal boron nitride (hBN).
The diffuser, called aero-BN, is made of a semi-transparent web of randomly arranged and interconnected hBN hollow microtubes, and consists of more than 99.99 percent air. The three coloured laser beams penetrate deeply into the diffuser, where they are strongly and randomly scattered multiple times by the nanoscopic walls of the microtubes.
In this way, the diffuser acts like an artificial fog, making the light more diffuse. At an optimum intensity of all three lasers, white light is emitted, and by varying the ratio of intensity of the coloured lasers, this method allows for the choice of a rainbow palette of colours.
Co-author of the study Felice Torrisi, from the Department of Chemistry at Imperial, said: “We have shown that hexagonal boron nitride flakes can be assembled into a micro-scaffold that converts laser light into a white light source suitable for low-power and high-intensity lighting applications, just like lightbulbs, with the advantage of operating across all the visible colours.
“We are currently looking into applying this technology for future high-brightness and low-power illumination systems, with an enormous range of applications from indoor lighting to aerospace.”
The high degree of scattering inside the fog also reduces the problem of ‘speckle’ - a contrast pattern usually caused by LDs that is uncomfortable for human vision, making it unsuitable for lighting applications. In the artificial fog, a large number of speckle patterns were superimposed and averaged out, so that they became invisible to the human eye.
Xinliang Feng, the Graphene Flagship's Work Package Leader for Functional Foams and Coatings, said: "This is an excellent example of how we can utilise the functionality of layered materials on the macroscopic scale. The foam is capable of withstanding extremely high-powered lasers, allowing for the creation of small-scale light sources with extremely high intensities."
‘Conversionless efficient and broadband laser light diffusers for high brightness illumination applications’ by F. Schütt et al; Nature Communications.































































.jpeg)














