Staggered Quantum Wells boost Yellow LED Efficiency
WHU team shows improved optoelectronic properties and crystal qualities by introducing an optimised quantum well structure
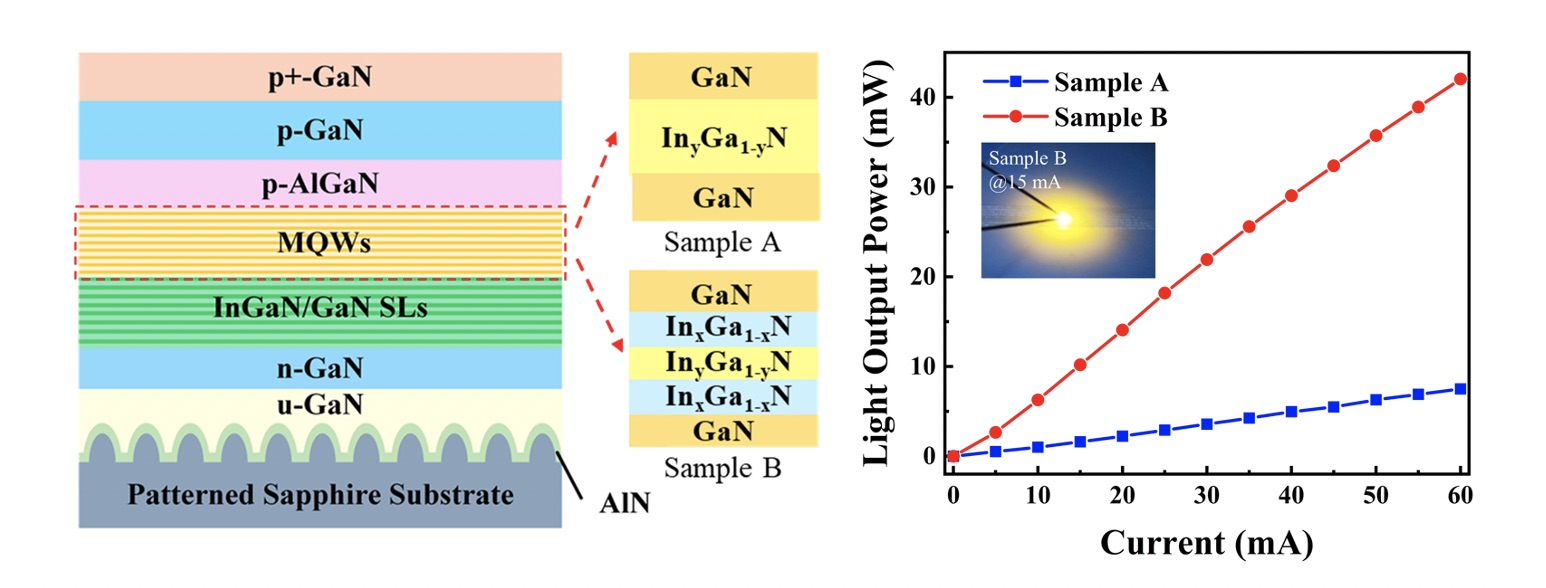
Researchers from Wuhan University in China have reported enhanced performance of InGaN-based yellow (~570 nm) LEDs with staggered quantum wells (QWs) structure. “We reveal that staggered QWs structure not only increases the electron–hole wavefunction overlap but also improves the crystal quality” said Shengjun Zhou, a professor at Wuhan University who directed the research.
III-Nitride emitters have been considered as an indispensable solid-state light source in the fields of lighting and display. By adjusting the indium content, one can obtain III-Nitride materials with tuneable bandgaps covering the wavelength range from ultraviolet to infrared. This platform enables monolithic integration of multi-coloured light-emitting pixels on a single chip and production of phosphor-free white LEDs that have attracted the interest of the public.
Moreover, InGaN-based micro-LEDs are currently one of the most promising candidates for next-generation high-resolution displays due to their excellent properties including high brightness, long lifetime, low power consumption, and fast response time. However, InGaN-based LEDs with emission wavelength above 540 nm exhibit much lower quantum efficiencies than their blue-emitting counterparts due to crystal quality degradation and the quantum-confined Stark effect.
The researchers expand the application of band engineering technique in long wavelength region and especially analyzes practical effect of staggered QWs on optoelectronic performance and crystal quality. Yellow (~570 nm) LEDs with staggered QWs exhibit smaller blue shifts, narrower full widths at half maximum (FWHM), and a 6.4-fold increase in light output power (LOP) compared to square QW LEDs.
Furthermore, staggered QWs exhibit superior material quality, including uniform layer thicknesses and elemental distributions analysed using atomic probe tomography (APT), time-resolved photoluminescence (TRPL) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) mapping spectroscopy. These indicate that both increased electron–hole wavefunction overlap and improved material quality contribute to the remarkable performance enhancement of staggered InGaN QW yellow LEDs.
'Rational construction of staggered InGaN quantum wells for efficient yellow light-emitting diodes' by Xiaoyu Zhao et al; Applied Physics Letters, 118, 182102 (2021).


































