Alternating V/III ratio superlattice enables high-quality AlN growth
Wuhan University researchers change dislocation behaviour with new approach to strain relaxation
Researchers from Wuhan University in China have reported the growth of high-quality AlN films on sapphire substrate enabled by an alternating V/III ratio superlattice. “The alternating V/III ratio AlN superlattice can be a valuable building block for the strain management and dislocation reduction in AlN epitaxy on sapphire,” said Shengjun Zhou, a professor at Wuhan University who directed the research.
AlGaN-based deep-ultraviolet (DUV) LEDs have attracted considerable attention in sterilisation and disinfection. Owing to the lack of economic bulk AlN, currently AlN/sapphire is the most preferable template for the building of AlGaN-based DUV LEDs. However, the lattice mismatch between AlN and sapphire results in high density of defects in the AlN epitaxy on sapphire, which has been a main performance bottleneck for AlGaN-based DUV LEDs.
The researchers from Wuhan University verified the feasibility of high-quality AlN epitaxy on sapphire at a relatively low temperature (1180degC) through introduction of the alternating V/III ratio AlN superlattice building block. They demonstrated that the alternating V/III ratio AlN superlattice plays a critical role in strain relaxation and dislocation reduction by changing the dislocation inclination behaviour.
The inclined threading dislocations can provide an effective misfit dislocation segment to relax the strain, thus eliminating the risk of wafer cracking during AlN growth. Furthermore, the inclined threading dislocations have a large probability of interaction with each other to realise further annihilation, contributing to a more significant annihilation of the threading dislocations.
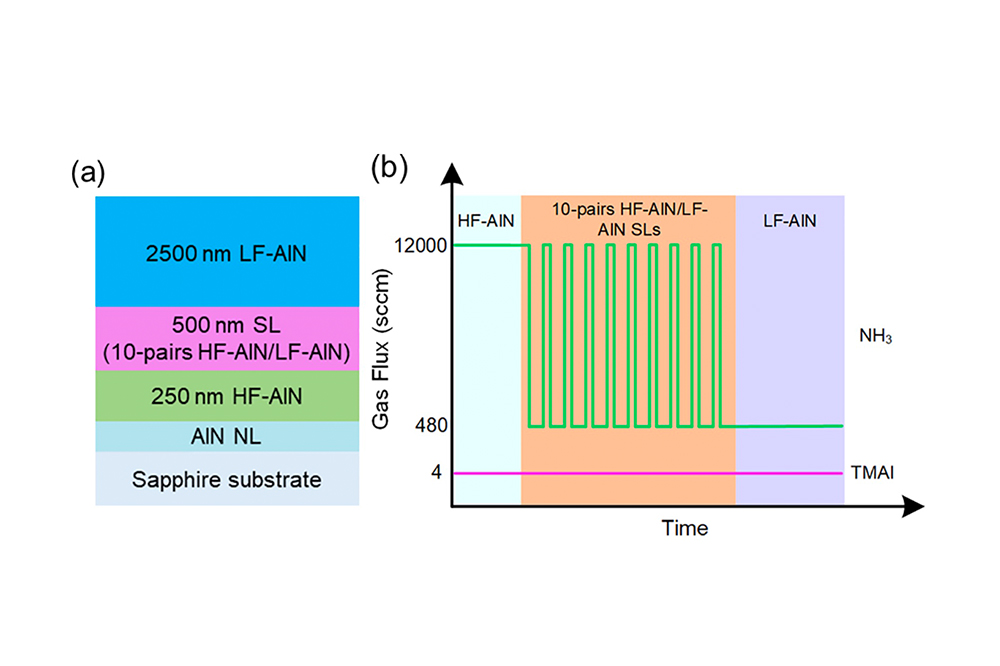
The picture above shows; (a) Schematic illustration of the AlN epitaxial structure with an alternating V/III ratio AlN SL. (b) Schematic illustration of the gas flux variation during AlN growth.
'Strain management and AlN crystal quality improvement with an alternating V/III ratio AlN superlattice' by Bin Tang et al, Applied Physics Letters 118, 262101 (2021)


































