Tuneable IR LED can identify a range of gases
Researcher develop technology that could turn smart phones into spectrometers
Scientsts have come up with an IR LED that is ‘tuneable’ to different wavelengths of light. The device can identify a suite of gases, potentially including lethal ones, improving the safety of firefighters, miners, the military, and your local plumber.
The technology has been developed by the University of Melbourne, the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, the University of California, Berkeley, and the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Transformative Meta-Optical Systems (TMOS). The work appeared in the journal, Nature.
IR spectrometers can be tuned to different wavelengths, giving a broad-spectrum analysis of a gas sample. However, these machines are bulky and expensive and not usually practical to take out of the laboratory and into the field.
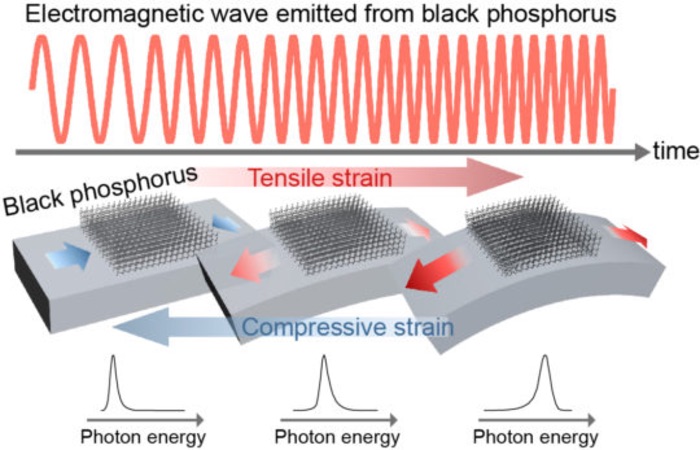
“Our new technology bonds a thin layer of black phosphorus crystals to a flexible, plastic-like substrate, allowing it to be bent in ways that cause the black phosphorus to emit light of different wavelengths essentially creating a tuneable infrared LED that allows for the detection of multiple materials,” Kenneth Crozier said, a professor at the University of Melbourne. “This technology could fit inside smartphones and become part of everyday use.”
For example, the bacteria found in meat release various gases as they multiply. The presence of these gases is a good indication that the meat is spoiling and is no longer fit for consumption.
“The device placed inside a fridge could send a notification that meat is going off. When pointed at a handbag, it could reveal whether the bag is made of real leather or a cheaper substitute,” said Crozier, who is also the deputy director of TMOS.
Current materials that are used for IR photodetectors and light emitting devices can be difficult to manufacture, in large part due to the need for multiple layers of perfectly linked crystals. This new black phosphorus technology requires just one layer allowing the device to be flexible, giving it unique properties when bent.
“The shift in black phosphorus' emission wavelength with bending is really quite dramatic, enabling the LED to be tuned across the mid-infrared,” said Ali Javey, from the University of California at Berkeley, whose group led the work.
Importantly, the device could make the work of firefighters, miners and military safer, allowing them to identify potentially lethal gases from safe distances as the ultra-thin, ultra-light devices can be placed on small drones. Flying such a drone over a building fire could tell firefighters what dangers they face and equipment they’ll need.
The low-cost technology could also make its way into devices for use by plumbers and building managers.
“Our IR photo detectors could be integrated into a camera so that we could look at our phone screen and ‘see’ gas leaks or emissions and be able to determine what kind of gas it is,” Crozier said.


































