EPC Releases latest Report on GaN Reliability
Report represents cumulative experience of five generations of technology
EPC has released its Phase-14 Reliability Report, documenting the strategy used to achieve its field reliability record.
The Phase-14 Reliability Report presents the strategy used to measure and predict lifetime based upon tests that force devices to fail under a variety of conditions. This information can be used to create stronger and higher performance products for applications such as lidar for autonomous cars, robotics, security, and drones, high power density computing, and satellites to name just a few.
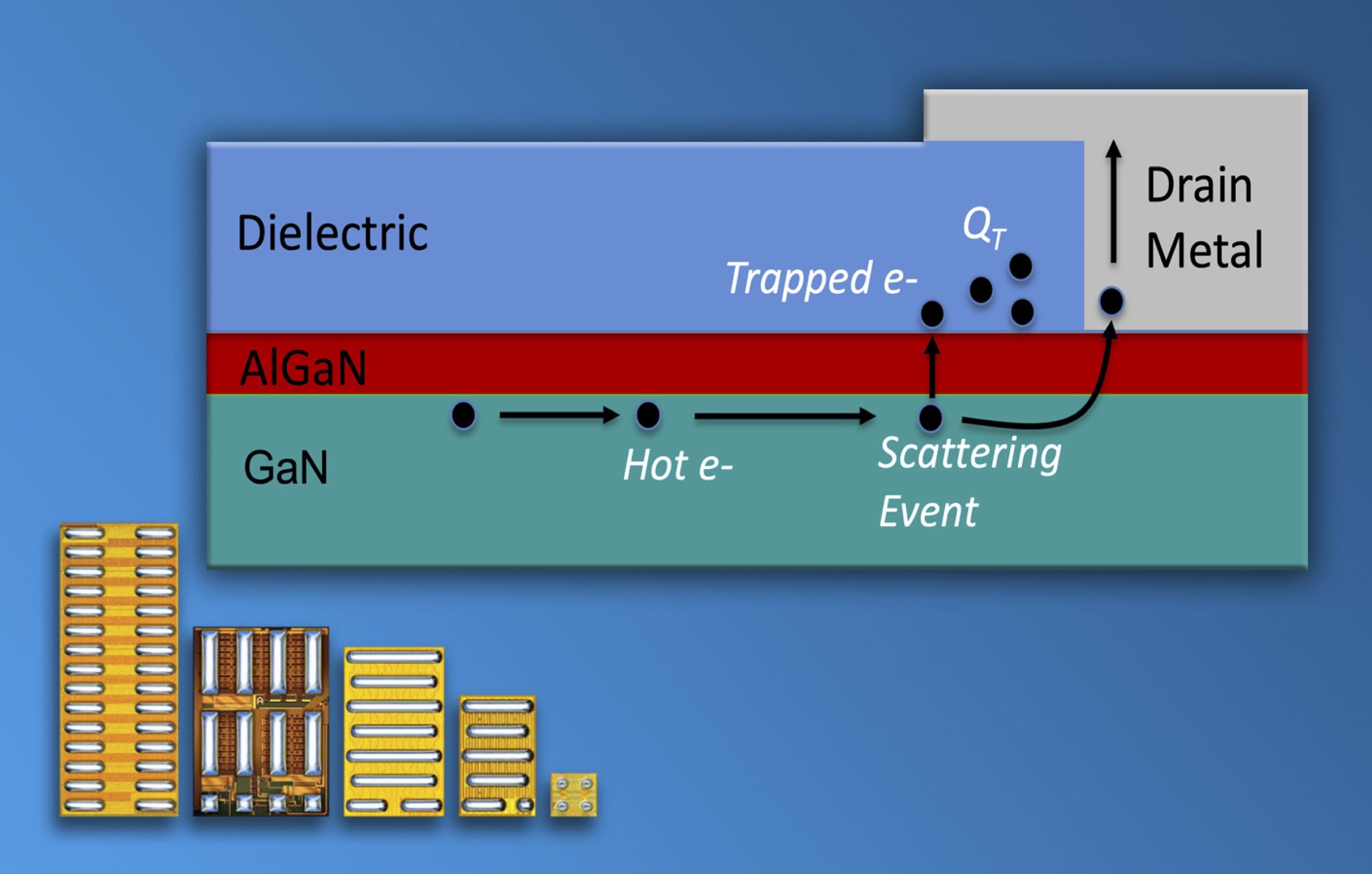
This report presents the results of testing eGaN devices to the point of failure, which provides the information to identify intrinsic failure mechanisms of the devices. By identifying these intrinsic failure mechanisms, deep knowledge of the behavior of a device over time, temperature, electrical or mechanical stress can be developed and used to create physics-based models that accurately project the safe operating life of a product over a more general set of operating conditions.
This report is divided into eight sections, each dealing with a different failure mechanism. These are Intrinsic failure mechanisms impacting the gate electrode of eGaN devices; Intrinsic mechanisms underlying dynamic RDS(on); Applying the physics-based model to common real-world use cases; Safe operating area (SOA); Testing devices to destruction under short-circuit conditions; Custom test to assess reliability over long-term lidar pulse stress conditions; Mechanical force stress testing; and Thermo-mechanical stress.
According to Alex Lidow, CEO and co-founder of EPC, “The release of EPC’s Phase-14 reliability report represents the cumulative experience of millions of devices and five generations of technology to lead to a deeper understanding of the behavior of GaN devices over a wide range of stress conditions.”


































