Quantum Well design Boosts Green LED Efficiency
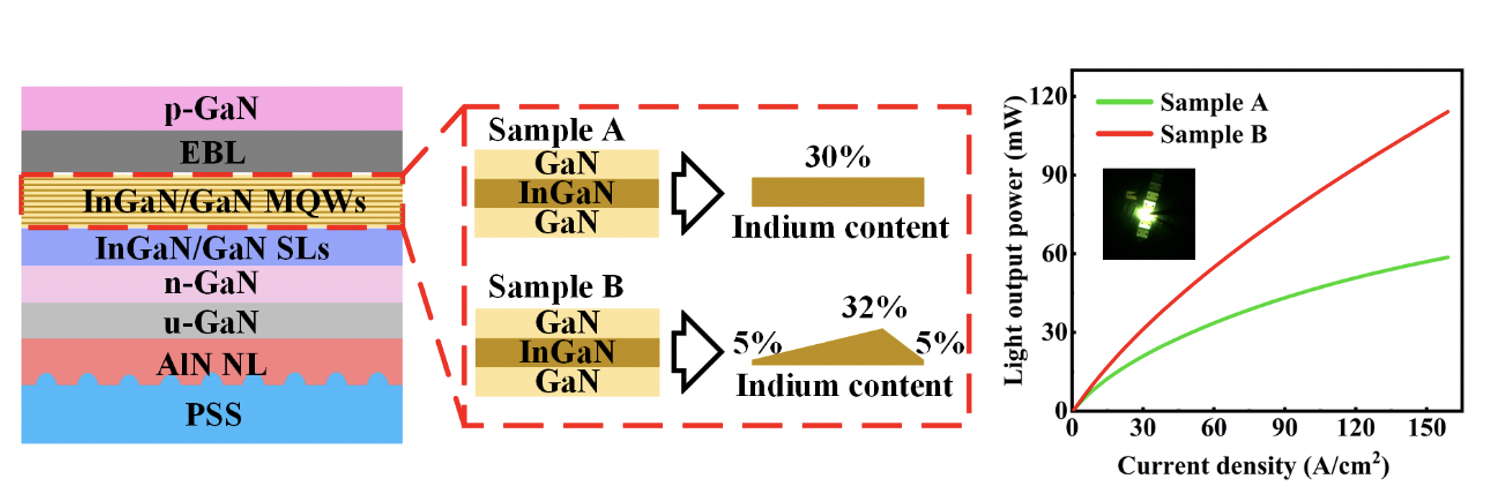
WHU team improves performance using an InGaN quantum well with gradually varying indium content
A research team from Wuhan University in China have made a major step toward improving the performance of green LEDs by a special design of quantum well. “Benefiting from the InGaN quantum well with gradually varying indium content, the green LEDs exhibited superior light output power (LOP) and lower efficiency droop,” said Shengjun Zhou, a professor at Wuhan University who directed the research.
The integration of multicolour emitters is extremely important for phosphor-free white light source and high-resolution full-colour display. The GaN-based blue LEDs and AlGaInP-based red LEDs have demonstrated superior optoelectronic performance. However, LEDs in the green spectral region suffer from poor efficiency (green gap) due to severe quantum-confined Stark effect (QCSE) and efficiency droop phenomenon, which limits the development of the integration of multicolour emitters.
The researchers demonstrated an InGaN quantum well with gradually varying indium content for green LEDs. The InGaN quantum well with gradually varying In content not only alleviates the QCSE, but also yields a low Auger recombination rate. Consequently, the gradual In content green LEDs exhibited increased LOP and reduced efficiency droop as compared to constant In content green LEDs.
When constant In content was replaced by gradual In content in InGaN quantum well, the LOP of green LED was increased from 33.9 mW to 55.2 mW at 60 A/cm2. Meanwhile, the efficiency droop of green LED was reduced from 61 percent to 37.6 percent at 150 A/cm2.
REF
'InGaN quantum well with gradually varying indium content for high-efficiency GaN-based green light-emitting diodes' by Shengjun Zhou et al; Optics Letters, 47(5) 1291-1294, 2022.