Canon develops durable perovskite QD ink
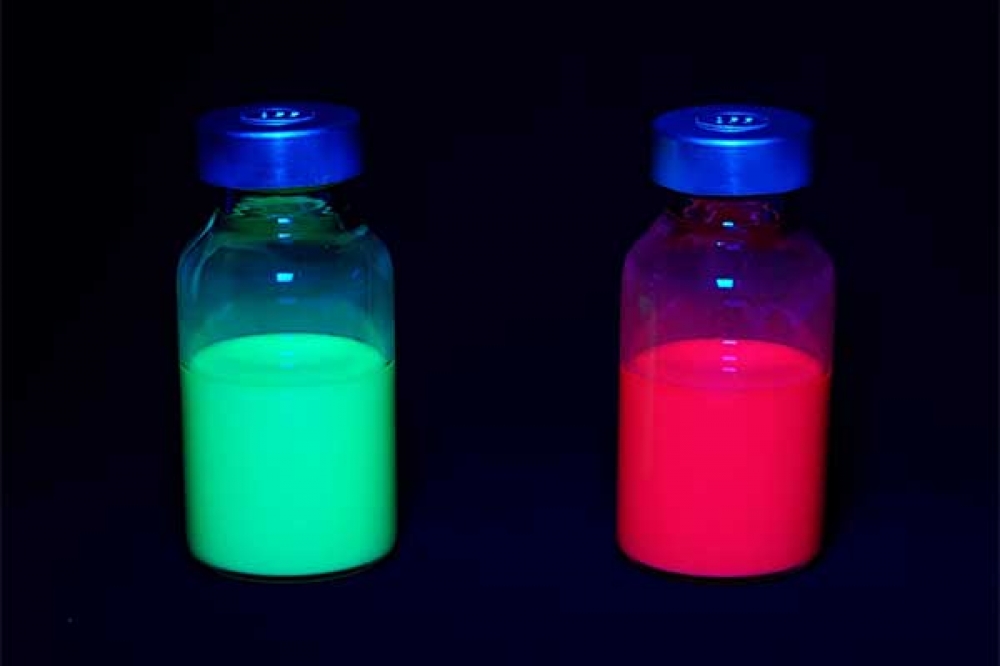

Improved durability using a shell structure shows potential for use in next-generation OLED displays
Canon has developed a quantum dot ink with a perovskite structure suitable for next-generation quantum-dot OLED displays, and has successfully demonstrated its practical durability.
Quantum dots convert the blue light of the light source into red and green. Compared with white light sources, quantum-dot technology makes possible red and green light with higher colour purity, thus enabling displays with a wider colour gamut.
Perovskite quantum dots are considered an effective Cd-free approach other than InP quantum dots. However, poor durability has been a barrier to practical use.
Now Canon says it has established a way to form a protective shell on its quantum dots, and achieved a T90=10,000 hours. T90 is time until the brightness reaches 90 percent of the initial value at 1,000nit (a unit indicating the degree of brightness), which is equivalent to the blue light brightness under actual use.
InP quantum-dot ink covers 88 percent of the colour gamut based on the ITU-R BT. 2020 recommendation. Canon says its perovskite quantum-dot inks can cover 94 percent4 of the gamut. In addition, the high efficiency of light use is expected to reduce power consumption of quantum dots by approximately 20 percent5 compared to conventional technology.