News Article
DISCO develops KABRA process for GaN wafers
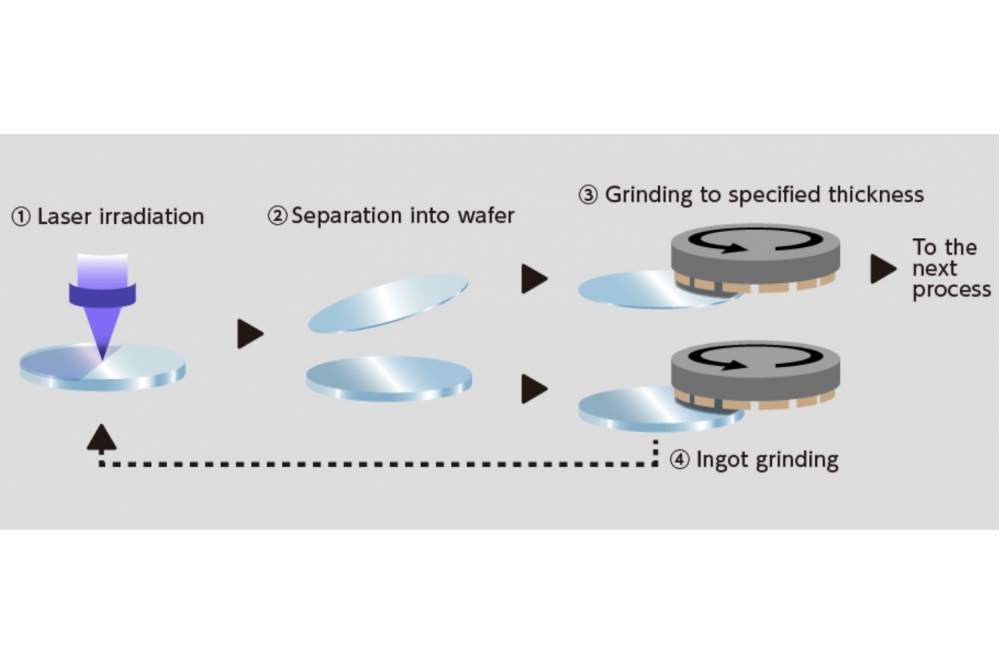
Process can increase the number of GaN wafers produced and decrease production time
DISCO Corporation has developed a KABRA ingot slicing method specially optimised for the production of GaN wafers.
In the KABRA process (shown above), a separation layer (KABRA layer) is formed at a specified depth by continuously irradiating an ingot with a laser, producing wafers starting from the KABRA layer.
This approach can increase the number of GaN wafers produced and decrease production time, according to DISCO.
GaN requires time for crystal growth, and is a very delicate material as the ingots produced are small in diameter and thin. Conventionally, the mainstream method to slice GaN ingots into wafers is to use a diamond wire saw. However, the are problems when slicing with a wire saw, such as the processing time, material loss at the sliced sections that is thicker than the thickness of the wire used, and a low number of wafers produced due to material loss from the lapping process which is done after slicing to planarise the surface.
From the time when the KABRA process was developed for the production of SiC wafers, DISCO says it has been receiving requests from many manufacturers to apply this process to GaN as well.
DISCO has since been putting effort into R&D in order to realise a KABRA process optimised for GaN, and has now introduced it for mass-production.