Nanoimprinted PSSA for efficient green mini-LEDs
WHU team enhances green mini-LEDs performance by introducing nanoimprinted patterned sapphire with silica array
Researchers from Wuhan University in China have made significant progress in improving the crystalline quality of GaN epitaxy and enhancing the efficiency of miniaturised light-emitting diodes (mini-LEDs) through the development of a nanoimprinted patterned sapphire with silica array (PSSA).
“Our proposed nanoimprinted PSSA substrate can effectively reduce the dislocation density of GaN epitaxy and thus significantly improve the crystalline quality. The green mini-LEDs on PSSA exhibit improved external quantum efficiency and light output power compared with mini-LEDs on conventional patterned sapphire substrates (PSS),” said Shengjun Zhou, a professor at Wuhan University who directed the research.
Mini-LEDs are gaining attention due to their high brightness, long lifetime, and potential applications in various sectors, such as head-up displays, visible light communication, augmented/virtual reality (AR/VR), and wearable devices. However, further improvements are necessary to fully realise the potential of mini-LEDs, particularly in achieving full-colour displays. One of the main challenges in the development of mini-LEDs is the quality of III-nitride epitaxy and the low light extraction efficiency (LEE).
Despite the fact that PSS has been widely used as a substrate for epitaxial growth of III-nitrides, this technique does not effectively address the refractive index difference between the sapphire/air and GaN/sapphire interfaces, which limits the outcoupling capability of sapphire patterns. In addition, the misorientation growth of GaN on PSS hinders further reduction of the threading dislocation density (TDD), which affects the improvement of GaN epitaxial crystalline quality.
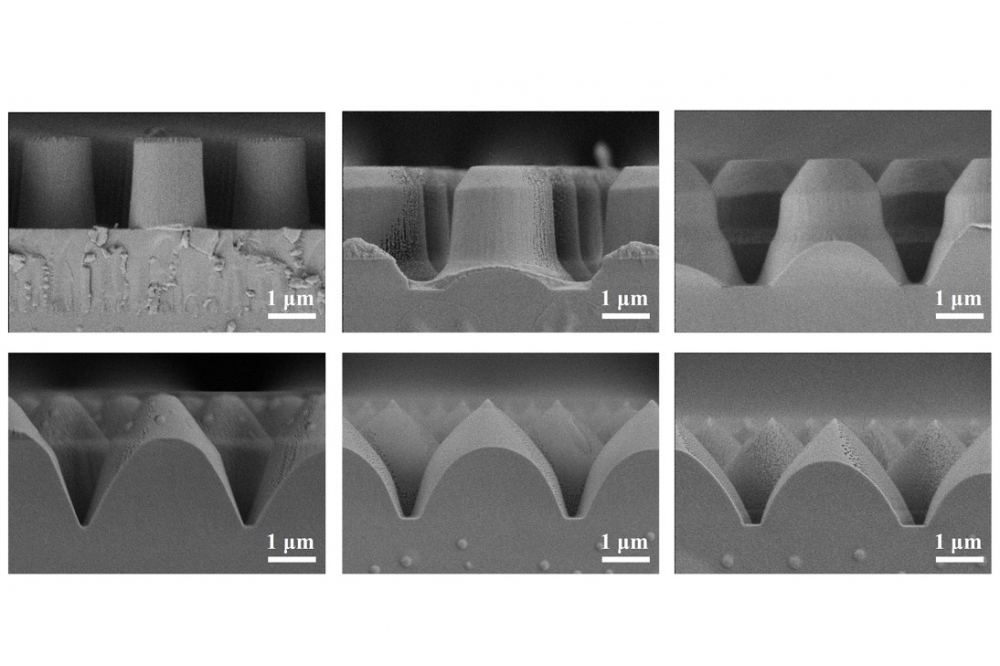
To address these issues, the researchers from Wuhan University proposed to fabricate PSSA by nanoimprinting technique to serve as a prominent substrate for highly efficient green mini-LEDs. The GaN epitaxial layers grown on PSSA exhibit lower TDD than those grown on PSS due to the superior vertical growth characteristics and reduced misfits of the coalescence boundaries during the 3D growth stage.
In addition, due to the large refractive index contrast between the PSSA and epilayers, the mini-LEDs on PSSA exhibit a higher LEE as compared to those on PSS. The use of nanoimprinted PSSA in mini-LEDs opens up new possibilities for the realisation of high-resolution full-colour displays. With the potential to address epitaxy quality and LEE challenges, this technology represents a significant contribution to the advancement of mini-LEDs and their applications in a wide range of fields.
Reference
'Nanoimprinted patterned sapphire with silica array for efficient InGaN-based green mini-LEDs' by Guoyi Tao et al; Optics Letters 48(16): 4292 (2023)