InP and TFLN: the way ahead for PICs?
IDTechEx has published a new report, ‘Silicon Photonics and Photonic Integrated Circuits 2024-2034: Market, Technologies, and Forecasts’ that explores emerging PIC materials including thin film lithium niobate and barium titanite, along with new applications such as AI.
The report says that photonic transceivers for AI are poised to become the largest demand source for PICs, driven by increasing need for high-speed, efficient data processing in AI applications. Additionally emerging technologies such as programmable photonics, photonic quantum computers, and co-packaged optics will redefine the capabilities and applications of PICs, unlocking new potentials in computing, communication, and sensing technologies.
Despite these advantages, the PIC market faces several challenges, according to the report. Cost management poses a critical issue, as designing and manufacturing PICs involves substantial initial investments. Large demand volumes are necessary to offset these expenses, and production lead times can extend over several months, complicating market responsiveness.
Material limitations
Material limitations complicate the development and performance of PICs, says IDTechEx. While silicon and silica are common in current PICs, they are not the most efficient materials for light sources or photodetectors. This necessitates the combination of silicon with III-V materials; however, this brings another challenge to the table – integration complexity. Combining different materials and components into a single PIC requires intricate engineering and manufacturing processes, ensuring compatibility and consistent performance across the various materials.
IDTechEx says that addressing material challenges is crucial for advancing PIC technology and expanding its use across different applications. Therefore, the future of PICs depends on exploring and adopting new materials to overcome these limitations.
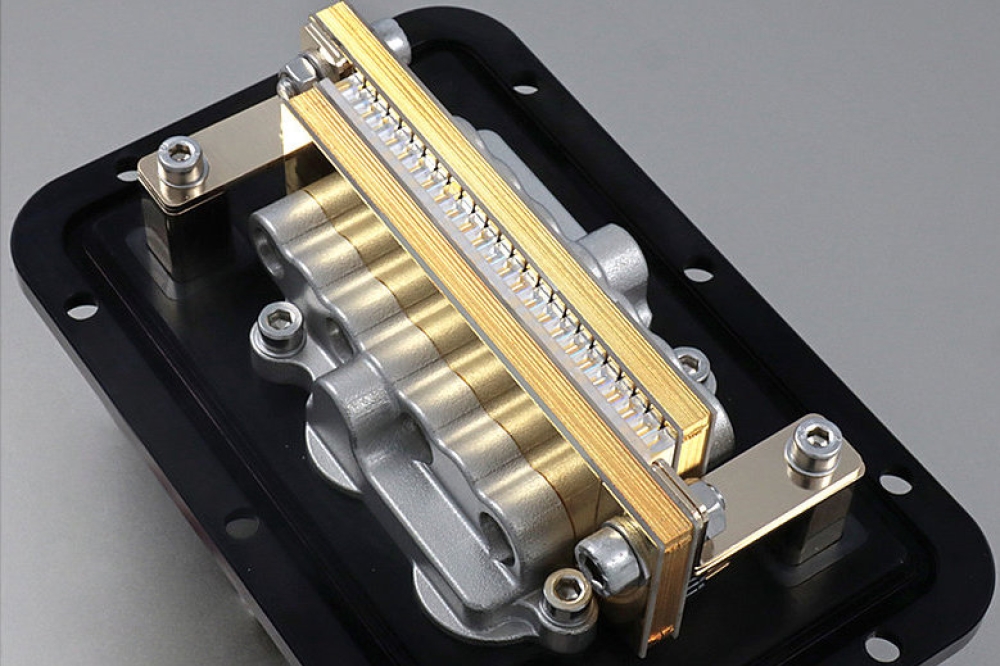
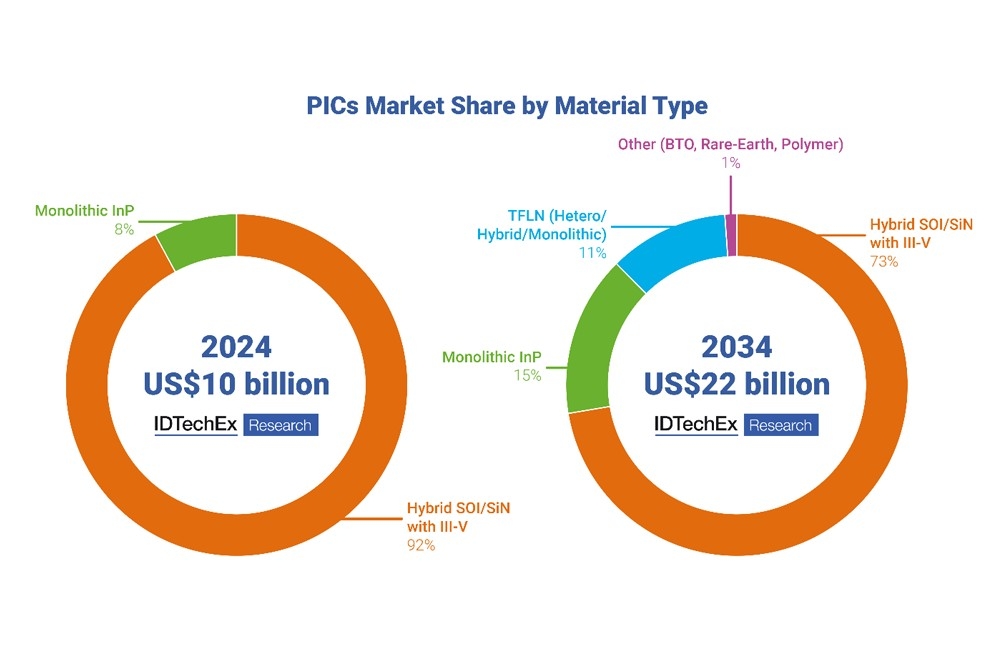
While silicon remains dominant, several emerging materials are gaining traction. Thin film lithium niobate (TFLN) offers moderate Pockels effect and low material loss, making it ideal for high-performance modulation applications, including quantum systems and future high-performance transceivers.
Monolithic InP continues to be significant due to its ability to detect and emit light, though it faces challenges related to high losses and costs. Barium Titanite (BTO), known for its superior modulation performance, is anticipated to find applications in quantum photonic systems where modulation efficiency is paramount.
SiN provides lower losses compared to other materials but comes with higher costs and larger device sizes due to its low refractive index, limiting its current widespread adoption.
IDTechEx forecasts that silicon will remain the dominant material in the PICs market. However, in the long run, monolithic InP and Thin-Film Lithium Niobate (TFLN) are projected to gain a growing market share.