Tanaka establishes new semiconductor bonding tech
High-density semiconductor mounting technique uses low-temperature fired paste for gold-to-gold bonding
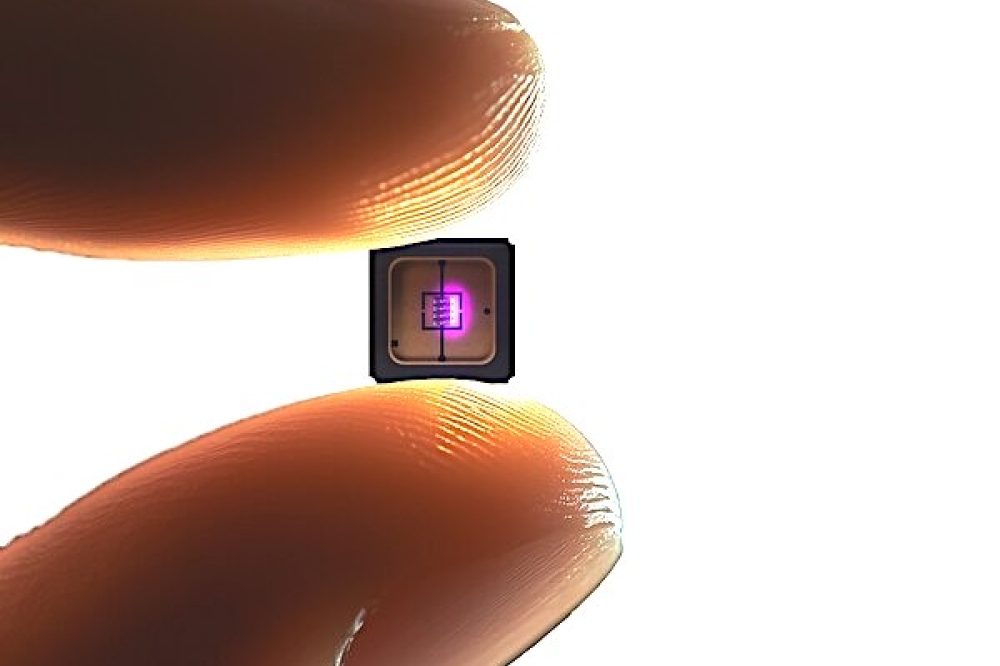
Tanaka Kikinzoku Kogyo, a Japanese developer of industrial precious metals products, has established a gold particle bonding technology for high-density mounting of semiconductors using its AuRoFUSE low-temperature fired paste for gold-to-gold bonding.
The technology enables miniaturisation of semiconductor wiring and greater integration (higher density) for various types of chips including LEDs and semiconductor lasers (LDs).
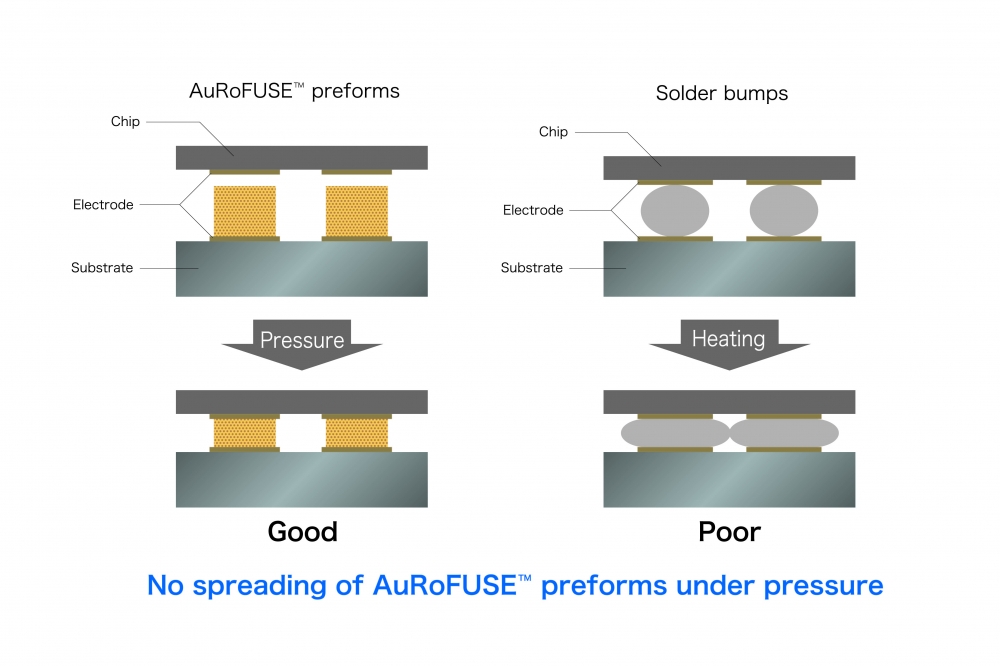
AuRoFUSE is a composition of submicron-sized gold particles and a solvent that creates a bonding material with low electrical resistance and high thermal conductivity to achieve metal bonding at low temperatures. Using AuRoFUSE preforms (dried paste forms), this technology can reach 4 μm fine-pitch mounting with 20 μm bumps, according to the company.
Formed through a thermocompression bonding process (20 MPa at 200°C for 10 seconds), AuRoFUSE preforms exhibit compression of approximately 10 percent in the compressive direction while showing minimal deformation in the horizontal direction. This gives them sufficient bonding strength1 for practical applications, making them suitable for use as gold bumps. With the main component being gold, which has a high level of chemical stability, AuRoFUSE preforms also provide excellent reliability after mounting.
Tanaka will present this technology at the 38th Spring Conference of the Japan Institute of Electronics Packaging to be held from March 13 to 15, 2024, at the Tokyo University of Science.