Researchers achieve higher growth quality with GaN on SOI

Insulating layer in SOI wafers also improves breakdown characteristics for power electronics
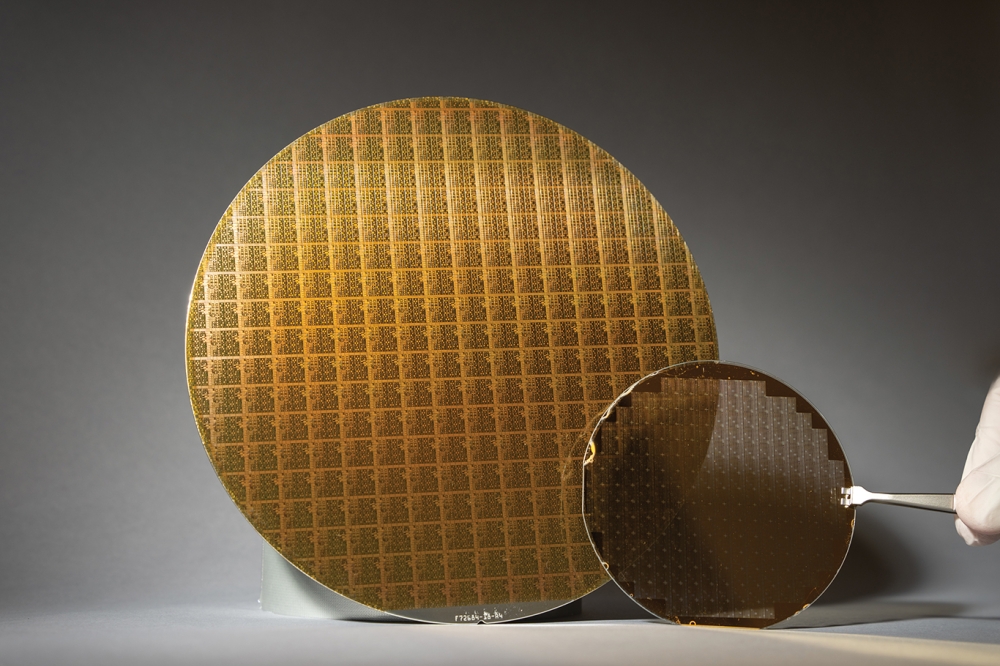
Working with Okmetic Oy and the Polish ITME, researchers at Aalto University in Finland have shown that SOI (Silicon On Insulator) wafers are suitable for growing GaN layers, reducing defects and strain compared to silicon substrates.
SOI wafers have a layer of silicon dioxide insulator sandwiched between two silicon layers in order to improve the capacitive and insulating characteristics of the wafer.
We used a standardised manufacturing process for comparing the wafer characteristics. GaN growth on SOI wafers produced a higher crystalline quality layer than on silicon wafers. In addition, the insulating layer in the SOI wafer improves breakdown characteristics, enabling the use of clearly higher voltages in power electronics. Similarly, in high frequency applications, the losses and crosstalk can be reduced", explains Jori Lemettinen, a doctoral candidate from the Department of Electronics and Nanoengineering.
GaN based components are becoming more common in power electronics and radio applications. The performance of GaN based devices can be improved by using a SOI wafer as the substrate", adds Academy Research Fellow Sami Suihkonen.
SOI wafers reduce the challenges of crystal growth
Growth of GaN on a silicon substrate is challenging because of the difference between the materials' coefficients of thermal expansion and lattice constants. These limit the crystalline quality that can be achieved and the maximum possible thickness of the produced layer.
"The research showed that the layered structure of an SOI wafer can act as a compliant substrate during GaN layer growth and thus reduce defects and strain in the grown layers", Lemettinen notes.
The work has been accepted for publication in the journal Semiconductor Science and Technology