Fuji Pigment to make Perovskite Quantum Dots
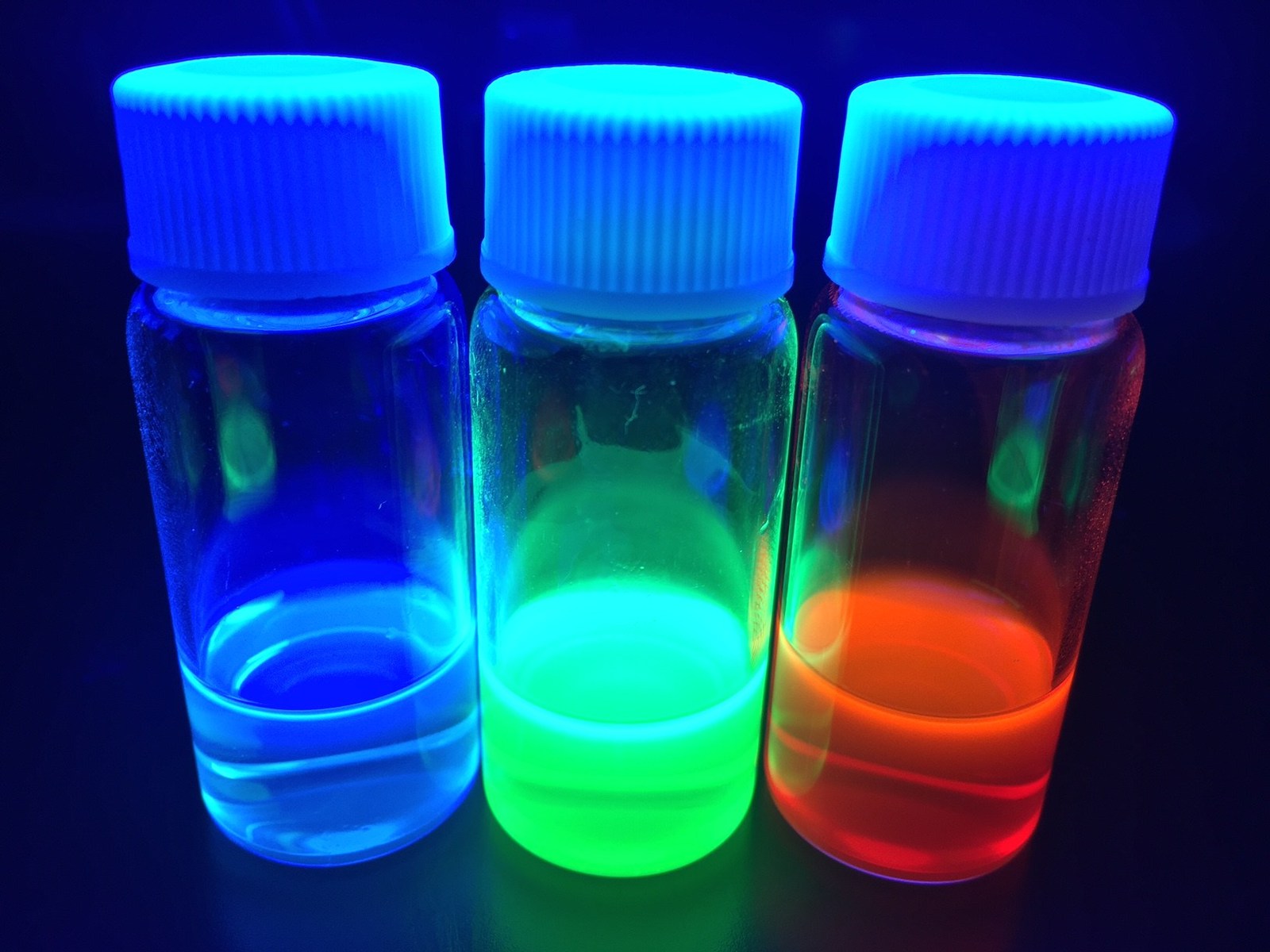

Emission spectra suggests they could be used in display, LED, and bio-imaging applications.
Quantum dots currently exist in many varieties. They are those made of semiconductor materials such as CdSe, CdS, InP, ZnS, InP/ZnS, CIS (CuInS2, CuInSe2), AgInS2 CIS/ZnS, and PbS that are expensive and (if they contain heavy metals such as cadmium, lead and selenium) toxic. And there are also carbon, graphene, and silicon quantum dots.
Fuji Pigment, based in Kawanishi City, Japan, synthesises and supplies all of these different quantum dots. But now Fuji researcher Ryohei Mori has developed a new type: perovskite quantum dots, and has succeeded in developing a large-scale synthesis process for them.
Fuji is thought to be the first company to commercialise perovskite quantum dots.
The chemical composition of perovskite quantum dots are either CsPbX3 or CH3NH3PbX3 (X= Cl, Br, I). Their quantum efficiency is 50 to 80 percent and their half width is 15 to 39 nm. Since the half width of the dots is small, they can be used in displays, lasers, LED and bio-imaging. The graph above shows the emission spectra of perovskite quantum dots under 420 nm of irradiation light.
The current base solvent for these new quantum dots is either hexane or toluene. However, finding alternative solvents is a challenge that is now being addressed. Furthermore, replacing lead with another element such as tin is under study. This entails widening the half width and decreasing the quantum efficiency. Moreover, Fuji Pigment is trying to coat perovskite quantum dot surface with either polymer or inorganic materials which would enhance the quantum dot resistance against water, light and heat.