Perovskites as catalysts
Scientists at TU Wien have produced a special perovskite suited to converting CO2 into other useful substances
If the CO2 content of the atmosphere is not to increase any further, carbon dioxide must be converted into something else. However, as CO2 is a very stable molecule, this can only be done with the help of special catalysts. The main problem with such catalysts has so far been their lack of stability: after a certain time, many materials lose their catalytic properties.
At TU Wien, research is being conducted on using perovskites as anode materials for their catalytic properties. Now scientists at TU Wien have succeeded in producing a special perovskite suited as a catalyst for converting CO2 into other useful substances, such as synthetic fuels.
How to close the carbon cycle
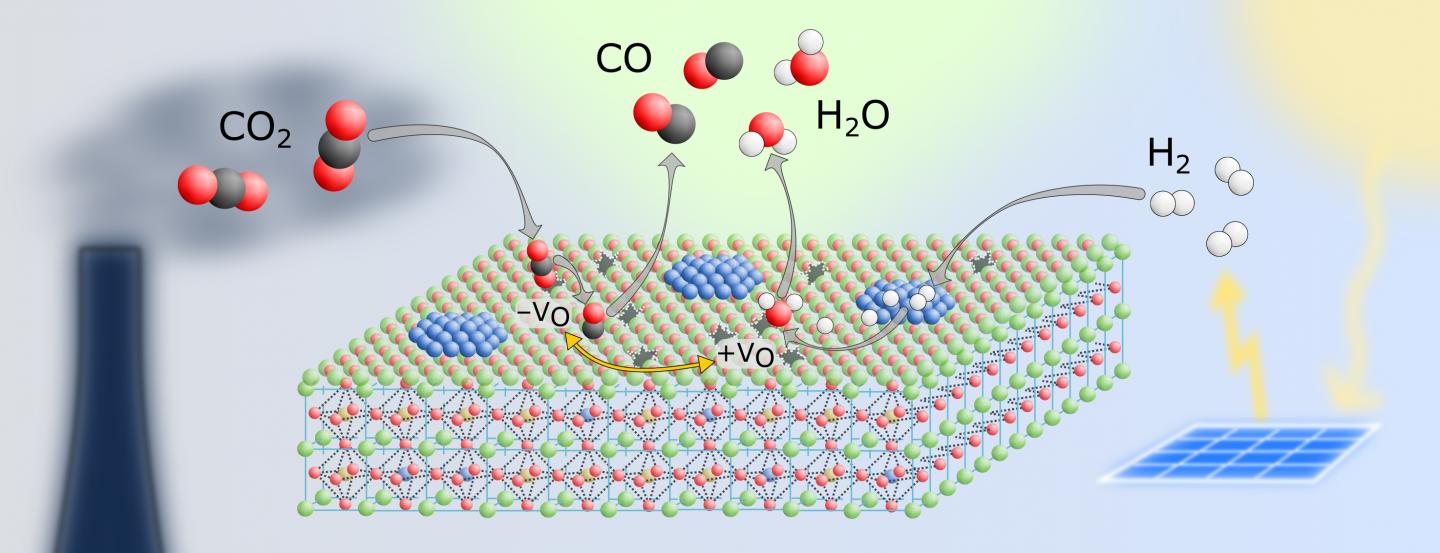
"We are interested in the so-called reverse water-gas shift reaction," says Christoph Rameshan from the Institute of Materials Chemistry at TU Wien. "In this process, carbon dioxide and hydrogen are converted into water and carbon monoxide. You can then process the carbon monoxide further, for example into methanol, other chemical base materials or even into fuel."
This reaction is not new, but it has not really been implemented on an industrial scale for CO2 utilisation. It takes place at high temperatures, which contributes to the fact that catalysts quickly break down. This is a particular problem when it comes to expensive materials, such as those containing rare metals.
Christoph Rameshan and his team investigated how to tailor a material from the class of perovskites specifically for this reaction, and he was successful: "We tried out a few things and finally came up with a perovskite made of cobalt, iron, calcium and neodymium that has excellent properties," says Rameshan.
Atoms migrating through the crystal
Because of its crystal structure, the perovskite allows certain atoms to migrate through it. For example, during catalysis, cobalt atoms from the inside of the material travel towards the surface and form tiny nanoparticles there, which are then particularly chemically active. At the same time, so-called oxygen vacancies form - positions in the crystal where an oxygen atom should actually sit. It is precisely at these vacant positions that CO2 molecules can dock particularly well, in order to then be dissociated into oxygen and carbon monoxide.
"We were able to show that our perovskite is significantly more stable than other catalysts," says Rameshan. "It also has the advantage that it can be regenerated: If its catalytic activity does wane after a certain time, you can simply restore it to its original state with the help of oxygen and continue to use it."
Initial assessments show that the catalyst is also economically promising. "It is more expensive than other catalysts, but only by about a factor of three, and it is much more durable," says Rameshan. "We would now like to try to replace the neodymium with something else, which could reduce the cost even further."
The industrial plant with built-in fuel production
Theoretically, you could use such technologies to get CO2 out of the atmosphere - but to do that you would first have to concentrate the carbon dioxide, and that requires a considerable amount of energy. It is therefore more efficient to first convert CO2 where it is produced in large quantities, such as in industrial plants. "You could simply add an additional reactor to existing plants that currently emit a lot of CO2, in which the CO2 is first converted into CO and then processed further," says Rameshan. Instead of harming the climate, such an industrial plant would then generate additional benefits.


































