OKI develops GaN lift off/bonding technology
Development paves the way to high current vertical GaN power devices
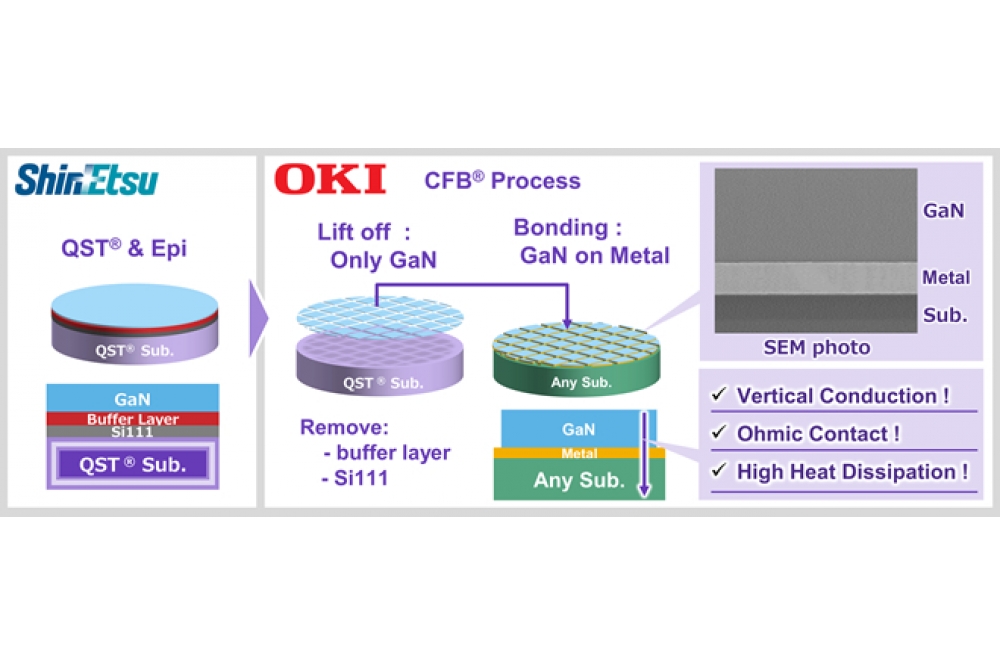
Japanese firm OKI, in collaboration with Shin-Etsu Chemical has announced the successful development of a technology that uses OKI's CFB (crystal film bonding) technology to lift off only the GaN functional layer from Shin-Etsu Chemical's QST (Qromis Substrate Technology) and bond it to a different material substrate.
The companies say this technology enables the vertical conduction of GaN and is expected to contribute to the realisation and commercialisation of vertical GaN power devices capable of controlling large currents.
The coefficient of thermal expansion of Shin-Etsu Chemical's QST substrate is equivalent to that of GaN. This means it can suppress warpage and cracking. It also enables the crystal growth of thick GaN films with high breakdown voltages even on wafers larger than 8 inches, enabling the production of wafers with larger diameters.
OKI's CFB technology can lift off only the GaN functional layer from the QST substrate while maintaining high device characteristics. The insulating buffer layer required for GaN crystal growth can be removed and bonded to various substrates via metal electrodes that allow ohmic contact. Bonding of these functional layers to a conductive substrate with high heat dissipation will enable both high heat dissipation and vertical conductivity, according to OKI.
In the future, the two companies aim to develop vertical GaN power devices through Shin-Etsu Chemical's provision of QST substrates or GaN grown QST substrates to companies manufacturing GaN devices, and OKI's provision of CFB technology through partnering and licensing.
OKI also hopes to use CFB technology to provide added value to semiconductor devices that go beyond the framework of single materials.






























