Sofradir IR detector on Japanese asteroid mission
![]()
An infrared detector developed by Sofradir was launched into space last week. The HgCdTe-based array is the "˜eye' of a hyperspectral microscope called MicrOmega being carried by the Japanese Space Agency's HAYABUSA-2 probe which will study the surface compounds of the "˜1999 JU3' asteroid.
"Sofradir is extremely proud to be part of this new deep space science mission that will surely excite every citizen and not only scientific teams, as we have lately witnessed with the ongoing ROSETTA mission", said Philippe Bensussan, Sofradir's chairman and CEO. "This attests to Sofradir's increasing technological leadership in producing reliable and high performance IR products for space applications."
The HAYABUSA-2 probe will reach the asteroid mid-2018, and will drop the MASCOT lander on the asteroid surface for in-situ analysis using the MicrOmega instrument. The mission will end in 2020 with asteroid ground samples being retrieved to Earth.
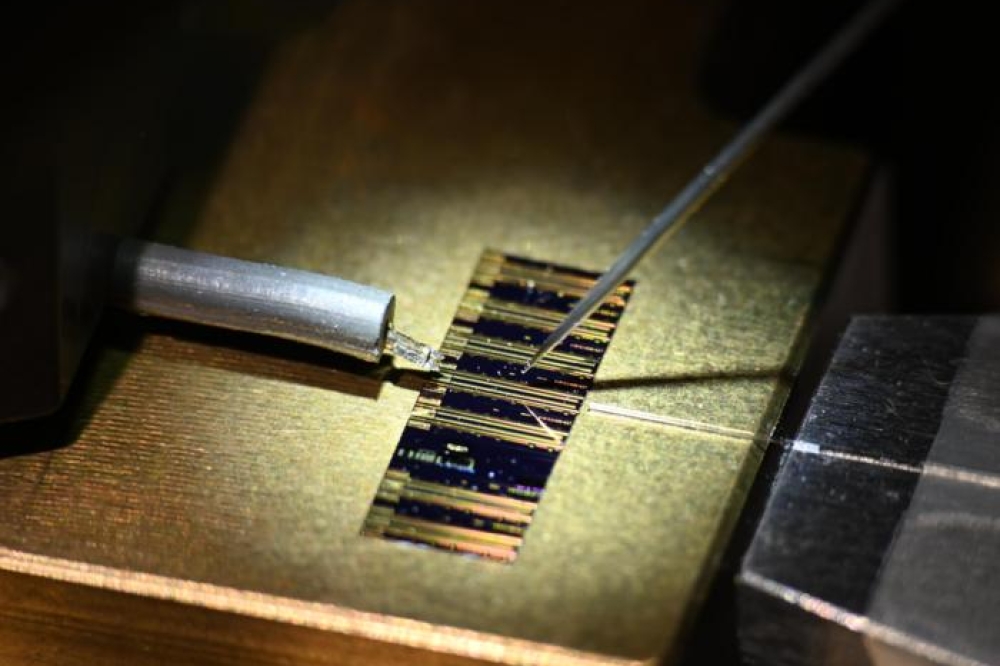
Sofradir's NEPTUNE detector was built into the MicrOmega IR microscope developed by IAS (Institut d'Astrophysique Spatiale at Orsay, France) with the support of CNES (Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales, the French space agency).
Thanks to its 30µm pitch 500x256 format HgCdTe array sensitive from Short Wave to low Mid Wave Infrared, the NEPTUNE hyperspectral detector will image the asteroid ground over 365 spectral bandwidths between 0.95µm and 3.65µm, enabling to determine its composition (mineral, organic, water).
Sofradir developed NEPTUNE detector more than ten years ago as an answer to the space-based and airborne hyperspectral or spectrometry applications.
Sofradir is a developer and manufacturer of advanced infrared detectors for military, space and industrial applications. Its IR product portfolio covers the spectrum from the visible and near infrared to very far infrared. The company pioneers developments in cooled IR detectors based on a high performance technology, Mercury Cadmium Telluride (MCT) to which InSb, InGaAs and Quantum Well Infrared Photodetector (QWIP) technologies are now added.