Japanese team finds new way to boost CIGS efficiency
Immersion of zinc-based buffer layer in ammonia water doubles conversion efficiency
![]()
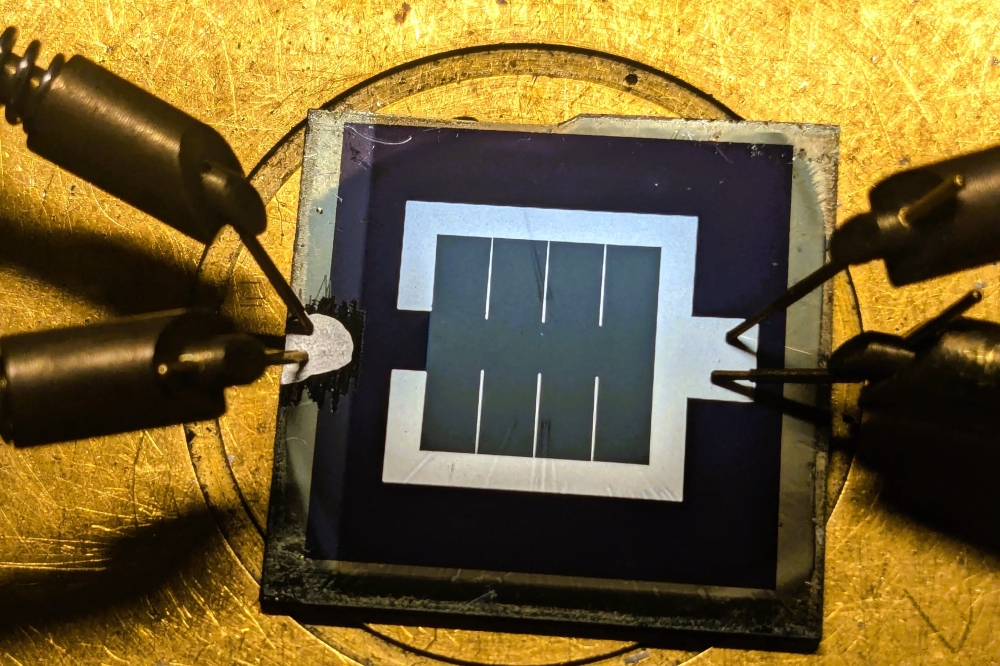
The conversion efficiency of CIGS solar cells is strongly affected by the buffer layer however its structure and precise influence have not been clarified.
Now Masanobu Izaki and colleagues at Toyohashi University, in collaboration with the Research Center for Photovoltaic Technologies, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, have analysed the structure of a zinc-based buffer layer in a CIGS solar cell at SPring8 - a synchrotron radiation facility, located in Hyogo Prefecture, Japan.
The researchers revealed the structure of the buffer layer and identified a way to improve the conversion efficiency. The study was published online in Progress in Photovoltaics on August 17, 2015.
"We analysed the structure of the buffer layer by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and other techniques. We found that the buffer layer was composed of two layers: an upper Zn(OH)2 layer and a lower Zn(S, O) layer. Moreover, the conversion efficiency was improved from 6.8 percent to 13.7 percent by removing the upper Zn(OH)2 layer," Izaki said.
![]()
In their article, the researchers described how to remove the upper Zn(OH)2 layer. The method is simple but impressive: quick immersion of a 120nm-thick film in ammonia led to a doubling of the solar conversion efficiency.
This study reveals the importance of the buffer layer structure and composition, and is expected to be a valuable step for the development of next-generation CIGS solar cells. It is anticipated that once CIGS cells are able to be mass produced at reduced cost, they will become a main player in the solar cell market.
'Structure of Chemically Deposited Zn(S, O, OH) Buffer Layer and the Effects on the Performance of Cu(In, Ga)Se2 Solar Cell', by Masanobu Izaki et al; Progress in Photovoltaics, 17 Aug 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/pip.2666