Fujitsu announces high output 75-110GHz GaN Power Amplifier
![]()
Fujitsu Limited and Fujitsu Laboratories have announced the development of a high power output GaN HEMT power amplifier for use in W-band (75-110GHz) transmissions, opening up the possibility of high-speed wireless communications of several Gbps in areas where fibre-optic cable is difficult to lay.
Evaluations of the newly developed power amplifier confirmed it to have 1.8 times increased output performance than before, which would translate to an increase of over 30 percent in transmission range when used in a high-speed wireless network.
A portion of this research was conducted as part of a project of the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) on "˜Agile Deployment Capability of Highly Resilient Optical and Radio Seamless Communication Systems'/ Details of this technology are being presented at Power Amplifiers for Wireless and Radio Applications (PAWR2016), opening January 24 in Austin, Texas.
Existing power amplifiers for high-frequency transmissions in the millimeter-wave band (30-300GHz), built using GaAs or CMOS semiconductors, are limited by their operating voltage to an output of about 0.1 W, and it has not been possible to increase this. GaN-HEMT power amplifiers have achieved high output performance in the microwave range (3-30 GHz), but the problem up until now was that their output performance declined in the W-band range.
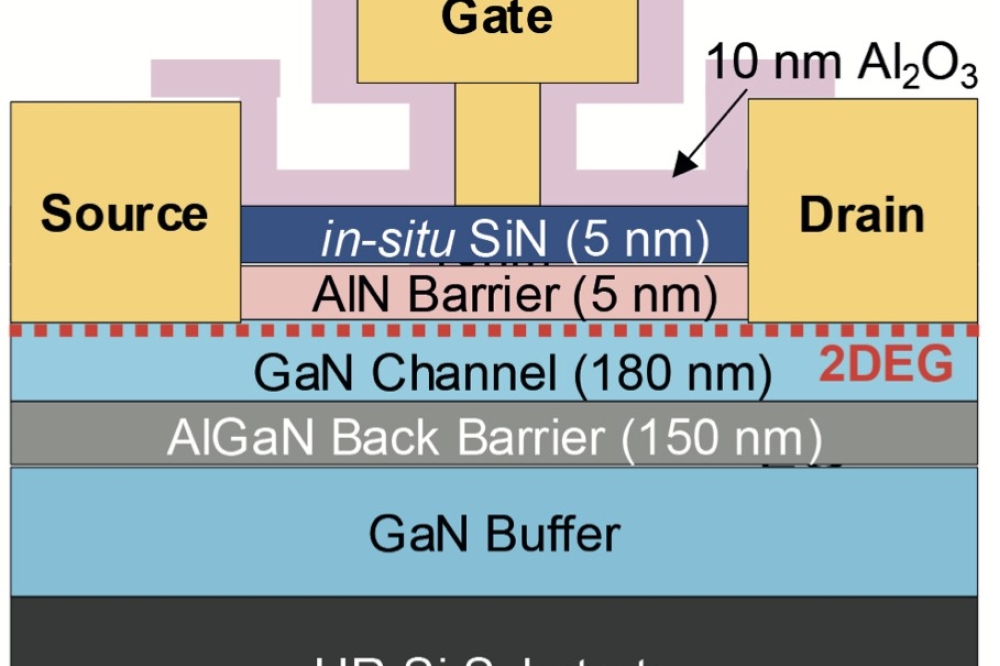
To solve these problems, Fujitsu developed a GaN-HEMT device with a unique structure capable of increasing output in the millimeter band (shown above). This uses a layer of InAlGaN, and double-layer SiN passivation film to increase current density by a factor of about 1.4, resulting in 3.0W of output power from a transistor per 1mm of gate width, at a high frequency of 100GHz. In developing this transistor, Fujitsu collaborated with Yasuyuki Miyamoto of the Tokyo Institute of Technology in developing a device-simulation technology.
Fujitsu's circuit uses pairs of GaN-HEMTs grouped together into compact, high-gain units with low power loss. These units are then connected in a series by the interstage circuits. An early prototype power amplifier had amplitude that multiplied its input by a factor of 80, producing 1.15W of output power. Power output per transistor, a measure of power-amplifier performance, was 3.6W per 1mm of gate width, the highest in the world, according to Fujitsu.
Fujitsu plans to apply this power amplifier technology to high-capacity long-range wireless communications, and to implement high-speed wireless communications systems that can be used for high-expediency temporary communications infrastructure for use during special events and when fibre-optic links have been broken in the event of disasters.