Glasgow team makes 'electronic skin' from GaAs
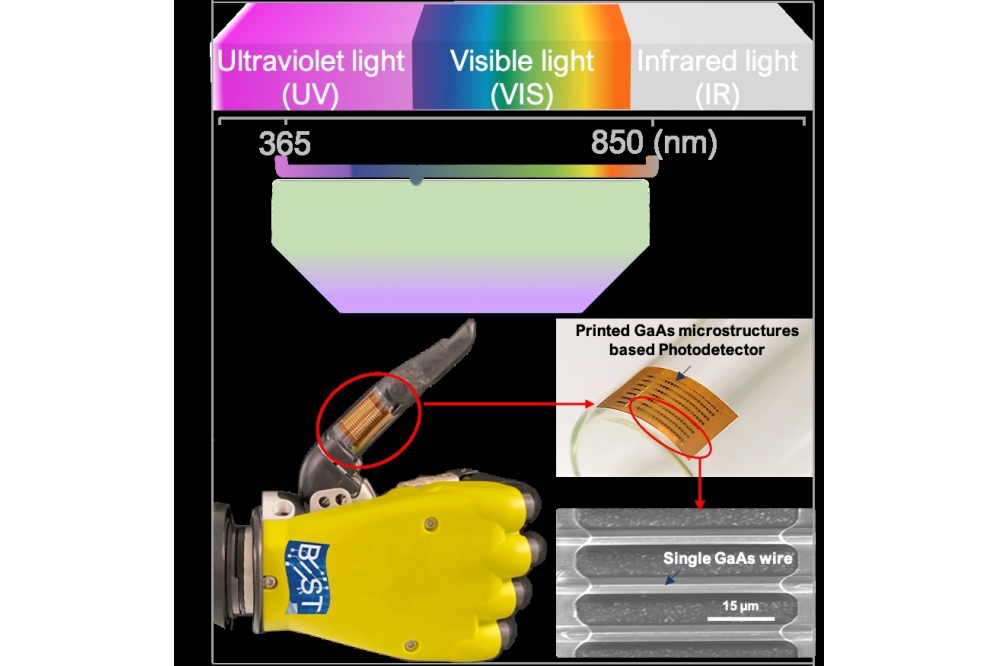
Flexible photodetector could give robots new capabilities
A new form of flexible photodetector could provide future robots with an electronic skin capable of ‘seeing’ light beyond the range of human vision.
A team of engineers from the University of Glasgow are behind the development, which involves a newly-developed method of printing microscale semiconductors made from GaAs onto a flexible plastic surface.
Their material provides performance equivalent to the best conventional photodetectors on the market, and are capable of withstanding hundreds of cycles of bending and flexing.
In a new paper published in the journal Advanced Materials Technology, the researchers outline how they developed the technology, which allows the skin to detect light from a broad range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
It builds on previous research from the team in which they developed a method of printing silicon circuitry directly onto the surface of flexible plastic, which enabled the creation of high-performance bendable electronics.
The Glasgow team are among the first to find a way to use GaAs on a flexible substrate.
They adapted their existing roll printing system to print GaAs electronics onto a flexible surface using arrays of wires that are 15µm in width.
That allowed them to create a new type of flexible photodetector capable of sensing light from the ultraviolet range, through the visible portion of the spectrum, to the infrared – all of it requiring extremely low power.
The system is capable of ultrafast response to light, taking just 2.5 milliseconds to measure light and 8 milliseconds to recover – a performance as good as the best non-flexible photodetectors currently available.
In order to test the system’s durability, they subjected the material to a rigorous set of tests in a machine designed to bend and twist it hundreds of times. Over the course of 500 cycles, the material demonstrated no significant loss in performance, suggesting it
Ravinder Dahiya of the University of Glasgow’s James Watt School of Engineering is the leader of the Bendable Electronics and Sensing Technologies (BEST) research group, which developed the skin.
Dahiya said: “We’ve been working for a number of years now to advance the capabilities of flexible electronics. We’ve found new ways to print electronics directly onto flexible surfaces, built electronic skin capable of feeling ‘pain’, and developed bendable electronics which can be powered by the sun or human sweat.
“This latest development is the first time we’ve been able to print GaAs onto flexible surfaces, opening up new avenues for our research.
“In the future, this type of light-sensitive flexible material could lend new abilities to robots. Mechanical arms used for manufacturing in light-sensitive environments, for example, could become capable of detecting when conditions change and the safety or effectiveness of their work is put at risk. Flexible, broad-spectrum photodetectors could also find use in a wide range of wireless communication technologies, where the fast transmission and response speeds we’ve tested are always in demand.
Ayoub Zumeit and Abhishek Dahiya from the BEST group, co-authors of the paper, added: “It could even be used to develop a wearable patch for humans to use to monitor exposure to UV light during sunny days, and provide a warning when users are at risk of getting sunburned.”
The team’s paper, titled ‘Printed GaAs Microstructures based Flexible High-Performance Broadband Photodetectors’, is published in Advanced Materials Technologies. The research was supported by funding from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).


































