InGaSb nanowires could improve high-speed communication
Chinese team synthesises nanowires with high carrier mobility and fast infrared light response
Chinese scientists have synthesised III-V compound nanowires with high carrier mobility and fast infrared light (IR) response, which they believe could help in high-speed 1550nm communication. Their findings were published in Nature Communications on April 10th.
According to quantum theory, 1550 nm IR has energy of ~ 0.8 eV, and can only be detected by semiconductors with bandgaps lower than 0.8 eV, such as germanium (0.66 eV) and III-V compound materials such as InxGa1-xAs (0.35-1.42 eV) and InxGa1-xSb (0.17-0.73 eV). However, those materials usually have crystal defects, which can cause reduce photoresponse performance.
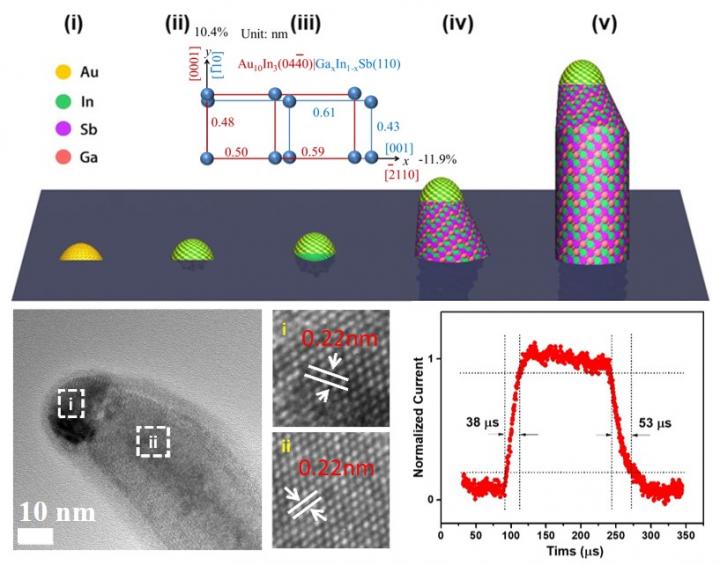
Scientists from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and their collaborators synthesised highly crystalline ternary In0.28Ga0.72Sb nanowires to demonstrate high carrier mobility and fast IR response.
In this study, the In0.28Ga0.72Sb nanowires (bandgap 0.69 eV) showed a high responsivity of 6000 A/W to IR with high response and decay times of 0.038ms and 0.053ms, respectively, which are some of the best times so far. The fast IR response speed can be attributed to the minimised crystal defects, as also illustrated by a high hole mobility of up to 200 cm2/Vs, according to Johnny C. Ho from CityU.
The minimised crystal defect is achieved by a 'catalyst epitaxy technology' first established by Ho's group. Briefly, the III-V compound nanowires are catalytically grown by a metal catalyst such as gold, nickel, etc.
"These catalyst nanoparticles play a key role in nanowire growth as the nanowires are synthesised layer by layer with the atoms well aligned with those in the catalyst," said Han Ning, a professor at IPE.
'Ultra-fast photodetectors based on high-mobility indium gallium antimonide nanowires' by Dapan Li et al; Nature Communications 10, Article number: 1664 (2019)


































