EPC launches solar optimiser reference design

GaN company Efficient Power Conversion Corporation (EPC) has announced the launch of the EPC9178, its latest GaN-baed reference design for photovoltaic (PV) optimisers.
The solution bridges the gap between micro-inverters and string inverters, offering improved energy efficiency and compatibility with existing infrastructure, according to EPC.
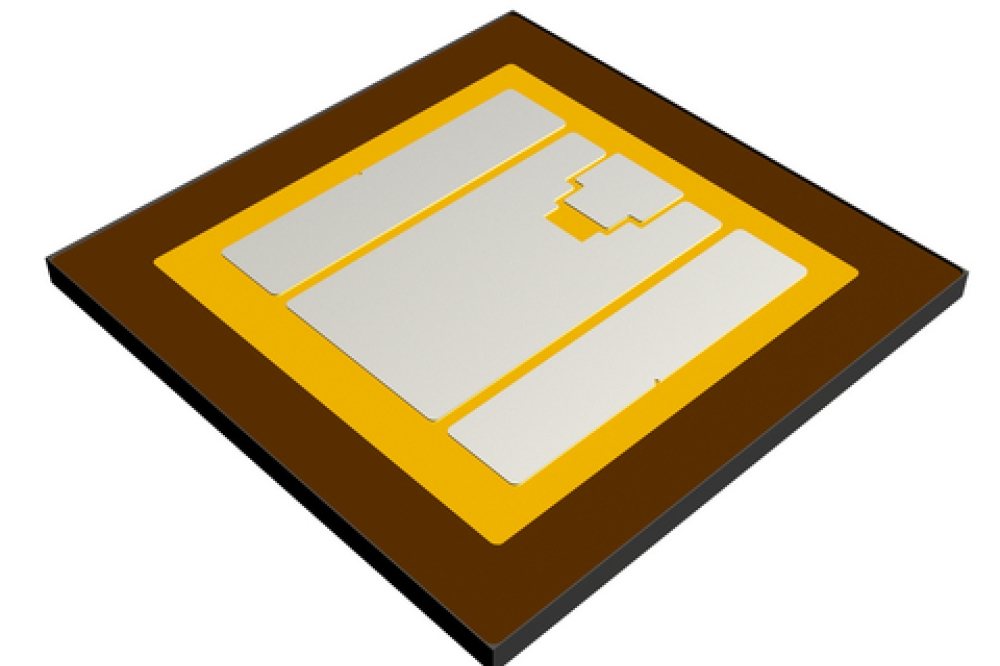
The EPC9178 reference design employs a back-to-back buck-boost converter topology, ensuring high energy harvesting for each solar panel, even under challenging conditions such as shading. It is powered by 100 V-rated EPC2306 eGaN FETs, with a low on-resistance (3.8 mΩ). An integrated LM5177 controller from Texas Instruments reduces design complexity and component count.
The high frequency operation at 450kHz minimises the size of passive components, resulting in a lightweight and space-saving solution. The design achieves up to 98 percent peak efficiency, reducing power losses and improving thermal management.
"The EPC9178 delivers a compact, high-performance, and reliable design that enables cost-effective solar energy systems," said Alex Lidow, CEO of EPC.
The EPC9178 evaluation boards are priced at $480.00. The EPC2306 is priced at $1.87/ea in 3Ku reels.