A new way to make lenticular displays?
Chinese team develops large-area periodic perovskite nanostructures suitable for lenticular printing laser displays
Lenticular printing provides an illusion of depth and shows varying images upon view angles, which is considered as a promising approach towards future stereoscopic displays.
To make lenticular-printing-based display, it is required to modulate the outcoupling direction of emission light rather than that of incident light. Ideally, the lenticular-lens-like structures would be integrated into the active layer of light-emitting devices.
Hybrid perovskite becomes a promising candidate for the investigation of lenticular printing display; however, it remains a challenge to make large-area periodic structures of perovskite materials especially with a feature size of wavelength scale.
Recently, Chuang Zhang,Yong Sheng Zhao from Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuchen Wu from Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and their colleagues fabricated lead halide perovskite periodic structures via a space-confined solution growth method. The spatial resolution could be down to hundreds of nanometers while the substrate size up to several centimetres.
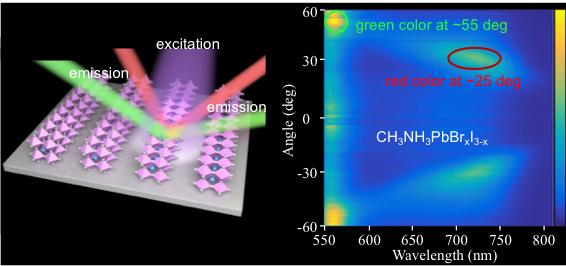
These structures were able to not only modulate the reflection of visible light, but also control the angle of light emission from hybrid perovskites. More importantly, the low-threshold lasing based on distributed feedback was observed from the periodic structures, and its narrow line-width offered possibility to realise the lenticular printing laser display, according to the wavelength-dependent outcoupling of emission colours.
A prototype of laser display panels was then realised based on the mixed halide perovskites, in which the green and red coloured images were obtained at high and low angles respectively. This work would shed light on the design and fabrication of perovskites materials for new types of display techniques.
'Large-area periodic lead halide perovskite nanostructures for lenticular printing laser displays' by Wang M et al; Sci. China Chem., 2020, DOI: 10.1007/s11426-020-9919-6.


































