1200V GaN HEMTs in the pipeline
Fraunhofer IAF reveals work on GaN-based alternatives to SiC MOSFETs
At the PCIM Europe exhibition in Nuremberg, researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF have revealed they are working on GaN-based HEMTs with blocking voltages up to and above 1200V for applications such as two-way charging of EVs. The aim is to replace SiC MOSFETs with a more cost-effective alternative.
Fraunhofer IAF is also pursuing several other approaches: the processing of GaN HEMTs on silicon substrates (GaN-on-Si HEMTs); the use of highly insulating carrier substrates such as sapphire, SiC or also GaN (GaN-on-insulator HEMTs); and the development of vertical GaN technologies.
Lateral GaN-on-Si HEMTs are already commercially available, but are limited to a blocking voltage of 650V due to limited GaN layer thicknesses. By continuously optimising the material and its processing (epitaxy, processing, structuring), researchers at Fraunhofer IAF have been able to demonstrate GaN-on-Si HEMTs with static blocking voltages of over 1200V.
In the second approach, the researchers replace the conductive Si with highly insulating carrier substrates such as sapphire, SiC or GaN, which virtually eliminates the voltage limit. Lateral GaN-on-sapphire HEMTs can be manufactured cost-effectively based on relevant preliminary work for LED applications and can be produced in existing production lines.
Vertical GaN technologies, in which the current flow runs vertically through the material layers, enable even greater performance with higher efficiency and integration capability at the same time. Within the next decade, the researchers at Fraunhofer IAF want to make vertical GaN power ICs suitable for industrial use.
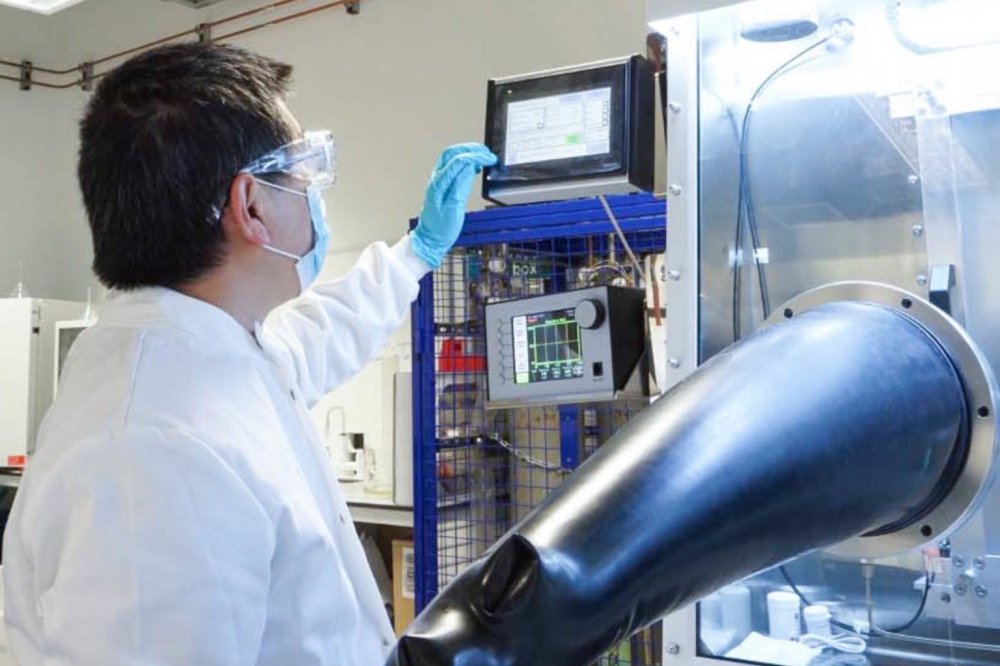
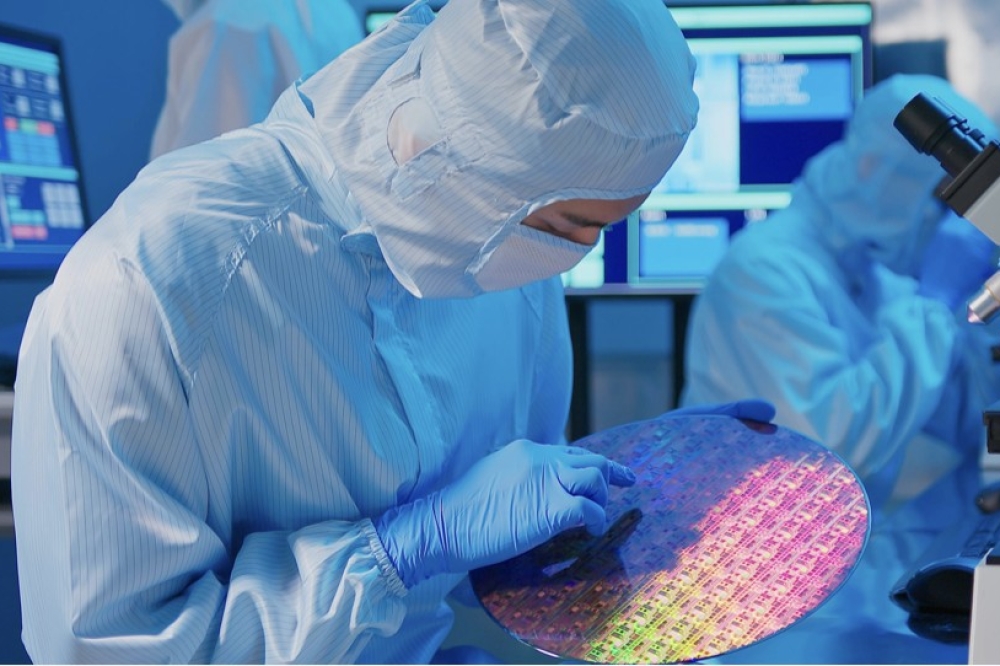
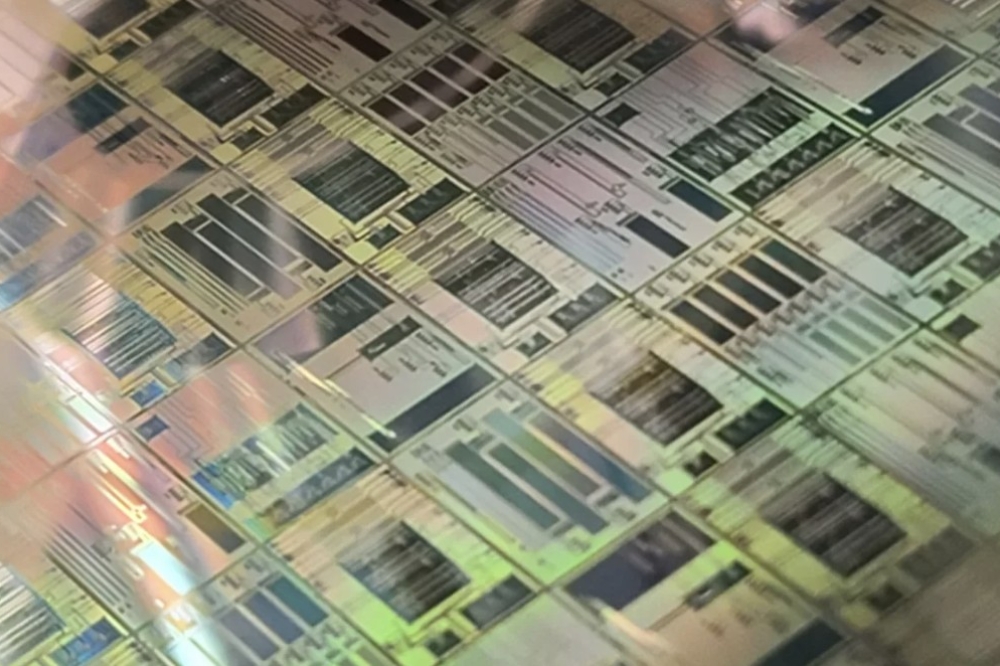
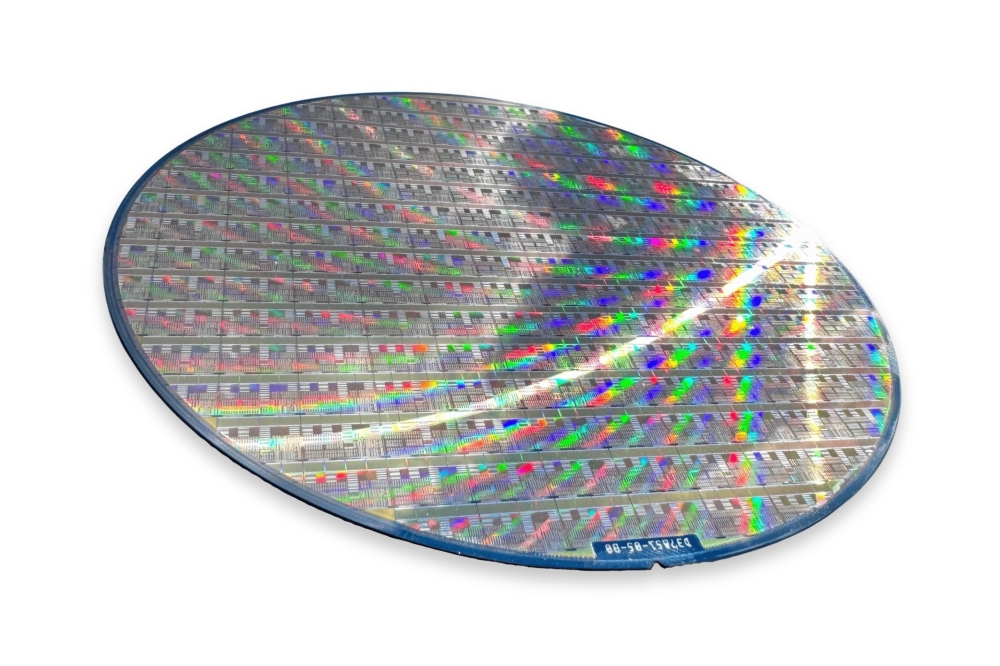
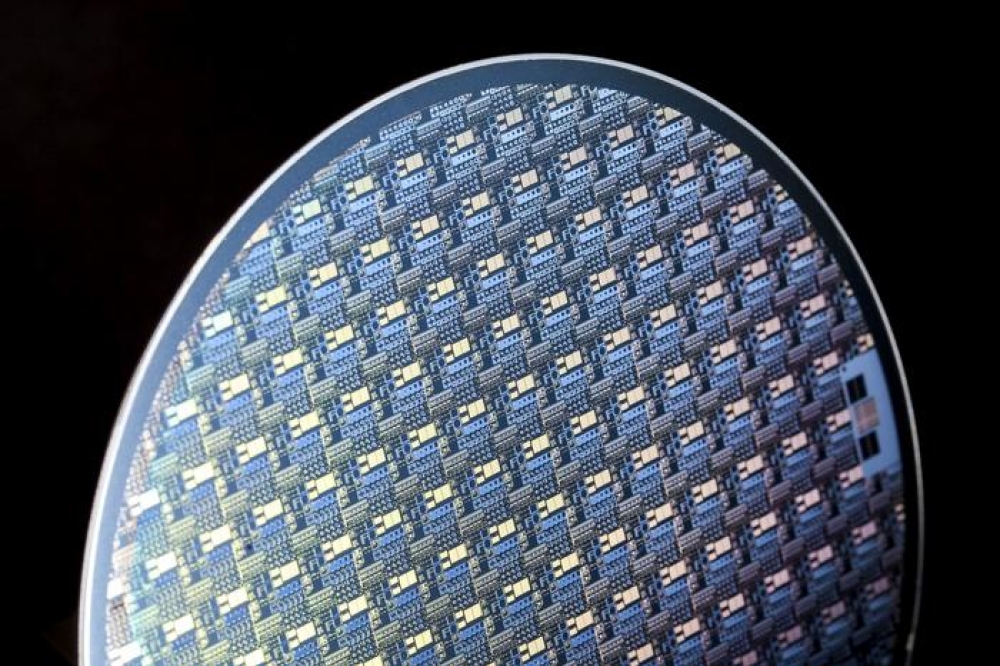
Pictured above: GaN-on-Si wafer comprising vertical components, developed by Fraunhofer IAF