Onsemi releases upgraded solar power modules

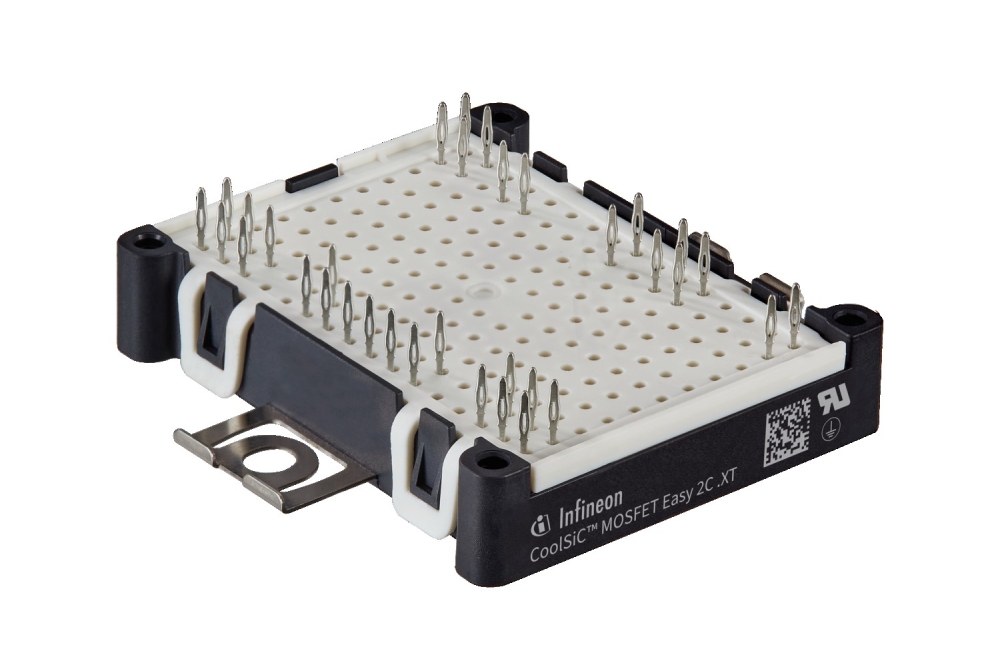
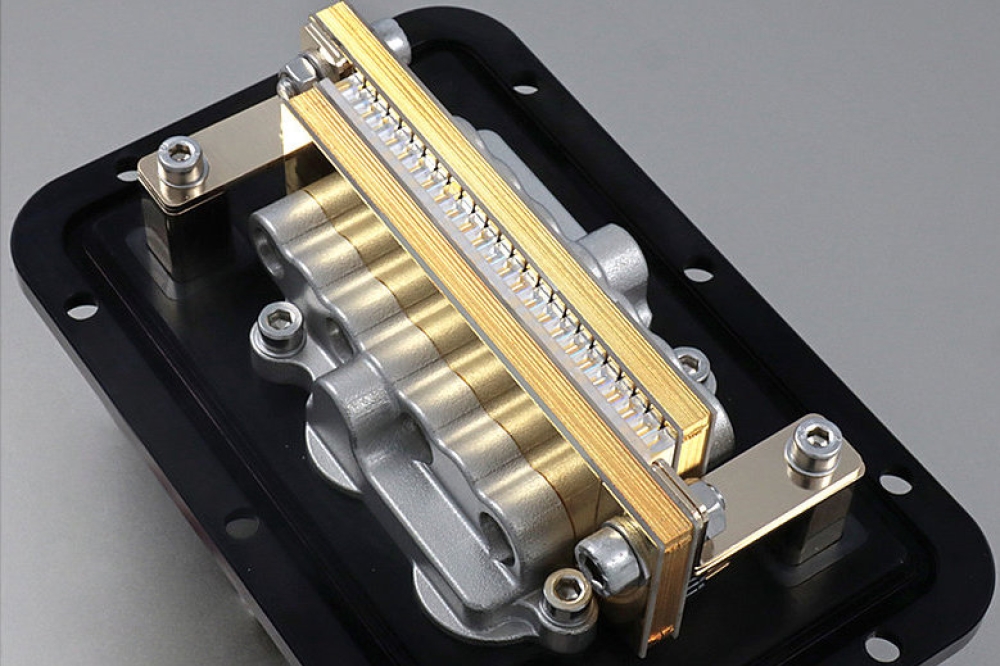
Onsemi has released a new generation silicon and SiC hybrid Power Integrated Modules (PIMs) in an F5BP package, suited to boost the power output of utility-scale solar string inverters or energy storage system (ESS) applications.
Compared to previous generations, the modules offer increased power density and higher efficiencies within the same footprint to increase the total system power of a solar inverter from 300kW up to 350kW.
This means a one-gigawatt (GW) capacity utility-scale solar farm using the latest generation modules can achieve an energy savings of nearly two megawatts (MW) per hour or the equivalent of powering more than 700 homes per year, according t the company. Additionally, fewer modules are required to achieve the same power threshold as the previous generation, which can reduce power device component costs by more than 25 percent.
“As a variable energy source dependant on sunlight, continual advances in increasing system efficiencies, reliability and advanced storage solutions are needed to be able to maintain the stability and reliability of global grids during peak and off-peak power demand,” said Sravan Vanaparthy, vice president, Industrial Power Division, Power Solutions Group, Onsemi. “A more efficient infrastructure increases adoption and assures us that, as more solar power generation is built out, less energy is wasted and pushes us forward on a path away from fossil fuels.”
The F5BP-PIMs are integrated with 1050V FS7 IGBT and the 1200V D3 EliteSiC diode to form a foundation that facilitates high voltage and high current power conversion while reducing power dissipation and increasing reliability. The FS7 IGBTs offer low turn-off losses and reduce switching losses by up to 8 percent, while the EliteSiC diodes provide superior switching performance and lower voltage flicker (VF) by 15 percent compared to previous generations.
These PIMs employ an I-type Neutral Point Clamp (INPC) for the inverter module and a flying capacitor topology for the boost module. The modules also use an optimised electrical layout and Direct Bonded Copper (DBC) substrates to reduce stray inductance and thermal resistance. A copper baseplate further decreases thermal resistance to the heat sink by 9.3 percent, ensuring the module remains cool under high operational loads.