How to make green ZnSeTe QD-LEDs brighter
QD-LEDs represent a highly promising next-generation display technology with InP and ZnSe QDs gaining research interest because they are relatively environmentally friendly.
InP QDs can flexibly tune their emission spectra by precisely controlling the crystal nucleus size, but their preparation relies on toxic and expensive phosphorus precursors. ZnSe QDs, by alloying with narrow-bandgap ZnTe to form ternary ZnSeTe QDs, can also achieve spectral tuning but they face performance bottlenecks in green and red devices due to the lack of effective defect passivation strategies.
Now Huaibin Shen and his colleagues from Henan University have shown in their study in the journal Science Bulletin, that it's possible to develop high performance, environmentally friendly green QD-LEDs.
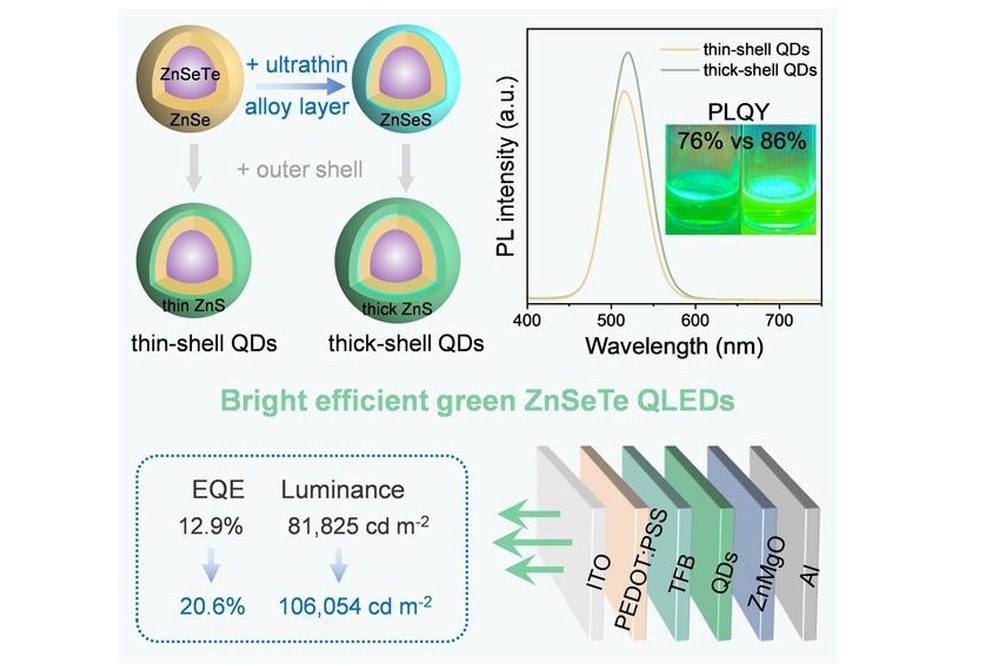
The research team used a low-temperature injection and high-temperature growth method and synthesised bright green-emissive thick-shell ZnSeTe/ZnSe/ZnSeS/ZnS QDs by inserting an ultrathin ZnSeS alloy interlayer to assist the growth of a thickened ZnS outer shell.
They show in the paper, 'Bright and efficient green ZnSeTe-based quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with EQE exceeding 20 percent' that the introduction of the ZnSeS interlayer alleviates the lattice mismatch between the ZnSe and ZnS, and the thickened shell further passivates the surface defects, thereby enhancing the radiative recombination efficiency and optical stability of ZnSeTe-based QDs.
Furthermore, they say this shell-tuning strategy results in a slightly upward shift in the energy level structure of the QDs, which facilitates the reduction of the hole injection barrier and the suppression of excess electron injection, ultimately promoting balanced carrier injection.
As a result, the peak external quantum efficiency (EQE) of the thick-shell green QD-LEDs demonstrated a substantial enhancement, rising from 12.9 percent to 20.6 percent, accompanied by a luminance exceeding 100,000 cd m−2, establishing a new record for the highest brightness among ZnSe- and ZnSeTe-based QD-LEDs.
Meanwhile, the operational stability of the devices improved significantly. The researchers say this structural design offers novel insights into the growth control and defect passivation of ZnSeTe-based QDs, laying a crucial foundation for the development of high-performance environmentally friendly electroluminescent devices.
Pictured above: Schematic depicting thin-shell and thick-shell ZnSeTe-based QDs induced respectively without and with an ultrathin ZnSeS interlayer. The thick-shell structure enhances the PLQY of the QDs, enabling brighter green emission and significantly improved brightness and efficiency of the QD-LED.