News Article
Reusable substrates for III-V multi-junction solar cells
Fraunhofer has been awarded for its work with CEA-LETI on developing reusable substrates for solar applications.
On December 5, 2011, Fraunhofer scientists were presented with the Franco German Business Award for their work with the Carnot-Institut Laboratoire d‘électronique des technologies de l‘information (CEA-LETI).
The photovoltaics industry is booming – more and more solar modules are appearing on rooftops, and even large-scale solar power plants are increasingly feeding power into the grid. Multi-junction solar cells are particularly efficient in this regard; they can achieve efficiencies of up to 43 percent - twice the level of conventional solar cells made of crystalline silicon.
The difference is that they consist of several semiconductor layers that combine to transform the entire spectrum of sunlight into electrical energy. This technology is used in concentrator photovoltaics. There, lenses focus the light of the sun 500 times onto tiny solar cells. These concentrator systems produce solar electricity on a large scale, particularly in solar power plants located in areas rich in sunlight. Among the producers of these plants is Soitec Solar based in Freiburg, Germany which is a former spinoff of the Fraunhofer Institute or Solar Energy Systems ISE.
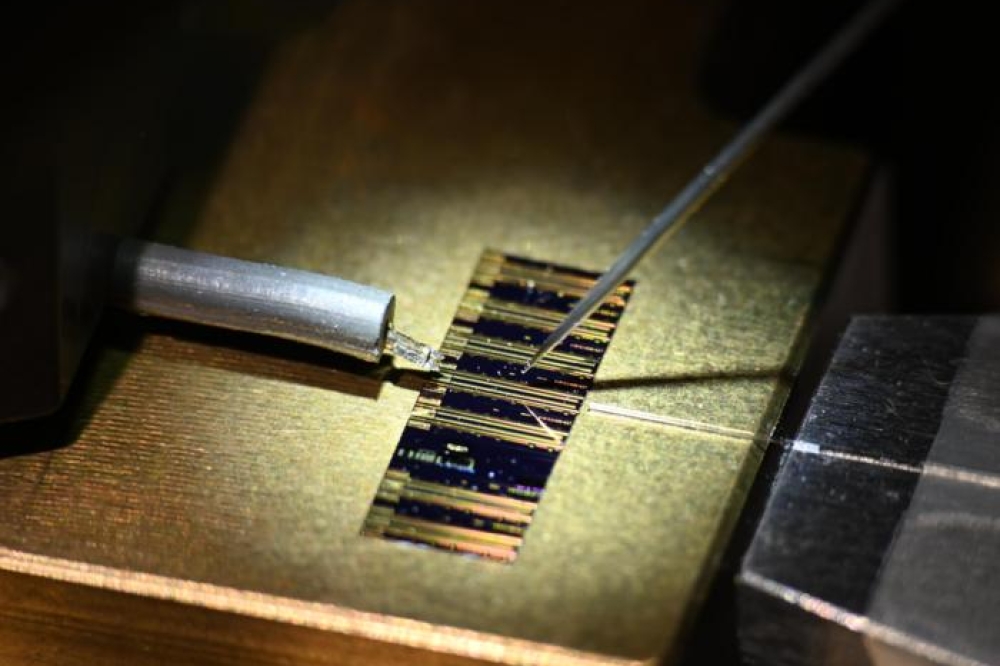
The multi-junction solar cells themselves consist of some 30 semiconductor layers built up, layer for layer, on ultra-pure crystals of germanium or GaAs. These materials are very costly, however. In a joint Franco-German project, researchers at ISE in Freiburg and their colleagues from CEA-LETI in Grenoble, France, are working to develop new substrates for multi-junction solar cells. The new technology replaces the expensive materials with reusable substrates.
Until now, Fraunhofer says solar cells had to remain on top of the the germanium or GaAs crystals. Now solar cells are removable from the new substrate which can be recycled several times. This way, the cost of producing solar cells can be reduced by up to 20 percent.
"In the Solar-Bond project, two high-tech institutes have combined their skills,“ according to Frank Dimroth, Head of Department III-V - Epitaxy and Solar Cells at Fraunhofer ISE. "CEA-LETI is a leader in the microelectronics field and Fraunhofer ISE in photovoltaics.“
CEA-LETI grows the substrates and adapts the properties to the requirements involved in growing multi-junction solar cells. The Fraunhofer scientists then apply the solar cells to these substrates and process them to create ready-to-use devices. The researchers are also working closely with Soitec; in the future, the new solar cells will be used in their concentrator modules.
The scientists were honoured for their international research on December 5, 2011, in Paris with the Franco-German Business Award 2011, presented by the Franco-German Chamber of Commerce and Industry AHK.
The business award is presented in recognition of best practices over the past two years. Patrons of the award are the French Minister of Economy, Finance and Industry, François Baroin; and the German Federal Minister for Economics and Technology, Philipp Rösler.