MBE tool benefits from joint development
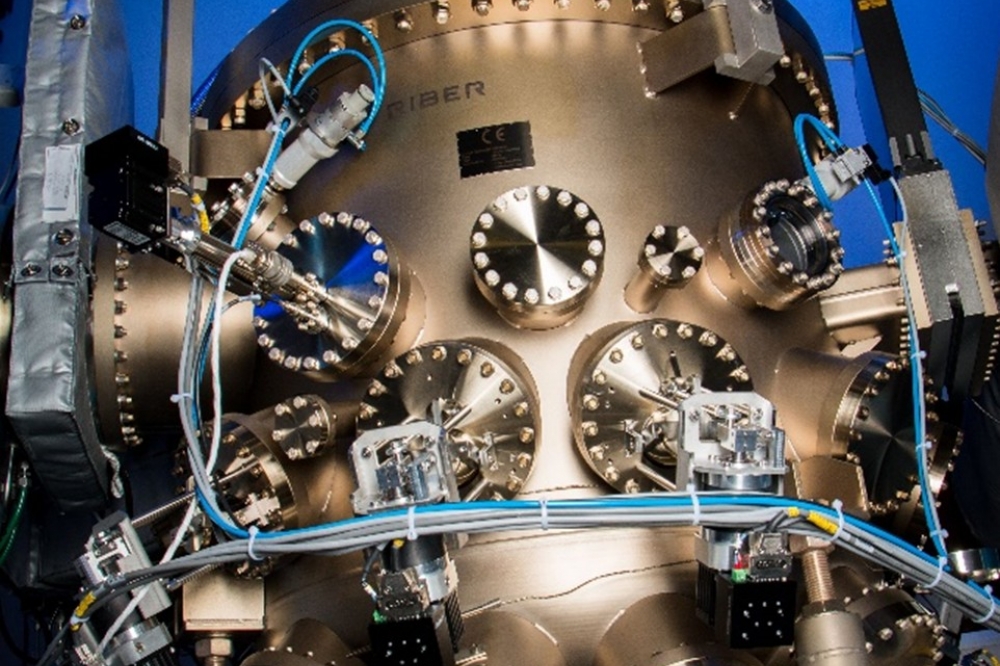
Riber says that partnership with French lab is key to new MBE 49 machine's success
Riber says its latest Asian order for an MBE 49 production machine for element III nitride applications (GaN, AlN) is a clear technological and commercial success for MBE in a competitive market, and a direct result of joint development work with the French lab CNRS - CRHEA.
The order results from R&D optimising the 200mm MBE 49 production machine in order to meet the production challenges of advanced GaN- and AlN-based optoelectronic components, according to Jean Louis Guyaux, Riber’s CTO. "It also confirms the relevance of our partnership initiated in 2018 with CNRS - CRHEA, Sophia Antipolis, France through the development of a joint laboratory. Riber is delighted with the excellent results of this collaboration and the exceptional performance achieved with the MBE 49 GaN, which is generating real interest from the scientific and industrial community worldwide," he said.
CRHEA director Philippe Boucaud adds: "Developing a technology that is ahead of its time on the market has required Riber to combine strategic vision with a willingness to invest in a bold and ambitious R&D program. CRHEA was a pioneer in GaN growth by MBE. It was therefore natural for it to make a long-term commitment to Riber, taking a significant risk on 200 mm GaN by MBE. The laboratory is proud to have been able to contribute to the development of GaN processes on a reactor like the MBE 49, which is a technological nugget. This is a remarkable success in the context of an exemplary partnership between CNRS and Riber."
The MBE 49 GaN is a fully automated production platform, compatible with ammonia and nitrogen plasma. It enables the production of high-quality optoelectronic and electronic devices: UV LEDs, MicroLEDs, RF components, N+ GaN ohmic contacts, etc.
The MBE 49 GaN is designed as a production tool for producing high-quality GaN layers on Si with improved voltages, considerably reduced RF losses and higher throughput with the required diameters.
Riber says that for the GaN process, MBE offers lower growth temperature than MOCVD, excellent p-doping quality, enhanced by the use of a valve cell, and excellent process control thanks to integrated in-situ instrumentation.
The extensive work carried out by the joint Riber / CRHEA laboratory has enabled the RF plasma source to be optimised to combine growth speed and deposition uniformity.
The joint Riber / CRHEA laboratory gives the community the opportunity to evaluate the structural, optical, and electronic qualities of epiwafer demonstrators, up to 200mm. The laboratory also opens its doors to all users wishing to see the machine in operation.