Doping barriers enhance DUV LED efficiency
WHU team boosts efficiency of AlGaN-based deep-ultraviolet LED with sandwich-like Si-doping quantum barriers
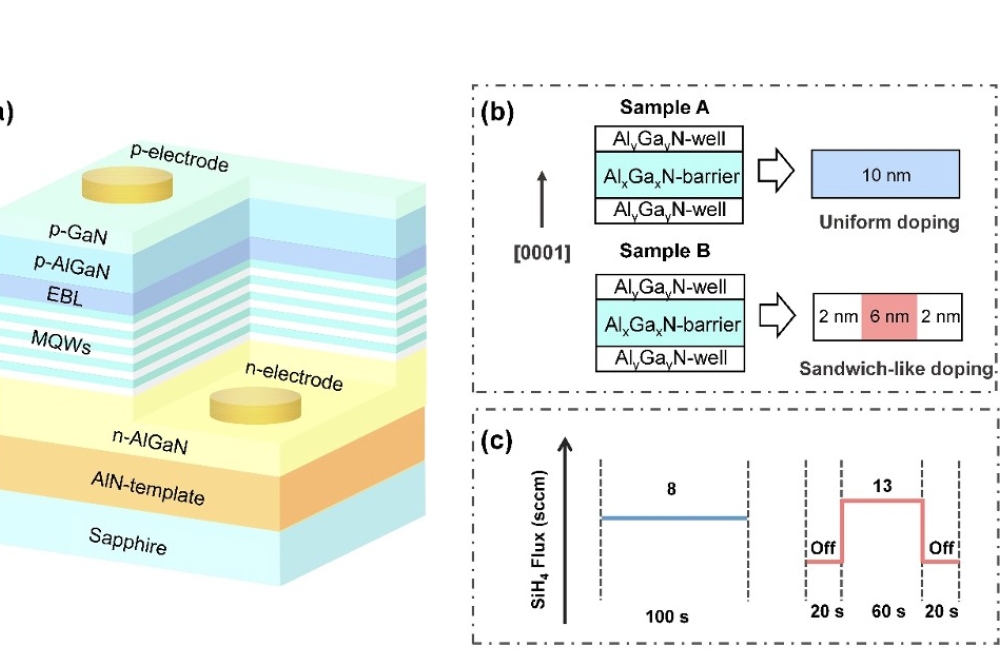
Researchers from Wuhan University in China have reported a feasible sandwich-like Si-doping (undoped-doped-undoped) scheme in Al0.6Ga0.4N quantum barriers (QBs) for improving the optoelectronic performances and reliability of deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (DUV LEDs).
“We reveal that the sandwich-like Si-doping scheme can improve interfacial quality in multiple quantum wells (MQWs), which can suppress the surface pits in MQWs induced by the heavily Si-doping QBs. As a result, compared with the conventional DUV LEDs with the uniform Si-doping structure, the proposed DUV LEDs reveal improvement in wall-plug efficiency, reduced by almost one order of magnitude in reverse leakage current (IR), and slower light output power (LOP) degradation after 168-h 100 mA-current-stress operation.” said professor Shengjun Zhou, who directed the research.
AlGaN-based DUV LEDs have garnered considerable attention due to their diverse range of applications. However, as a large polarisation-induced electric field exists in the QWs (on the order of MV/cm), which can reduce the electron–hole wave function overlap and further leads to decreased quantum efficiency in AlGaN-based DUV LEDs. Intentionally Si-doping QBs have been
adopted to mitigate the polarised electric field within QWs. Unfortunately, the proximity of the heavily Si-doped layers to the QWs risks introducing surface pits, which can deteriorate interfacial quality of MQWs, and thus hindering the improvement of device optoelectronic performance and accelerating the operation-induced reliability degradation.
To address these issues, the researchers introduce a sandwich-like Si-doping scheme and optimise doping levels and relative position of the doped barriers. Compared with the uniform Si-doping structure, this sandwich-like Si-doping scheme shows an improved interfacial quality in MQWs.
Besides, due to the introduction of undoped barriers, the reduced hole injection barriers facilitate holes move towards the n-side and more uniform carriers distribution in MQWs. Consequently, the proposed DUV LEDs show superior wall-plug efficiency (4 percent), IR reduced by almost one order of magnitude, and slower LOP degradation after 168-h 100 mA-current-stress operation.
With the potential to simultaneously improve the quantum efficiency and reliability, the sandwich-like doping scheme represents a significant contribution to the mass production of efficient AlGaN-based DUV LEDs.
'Strategically constructed AlGaN doping barriers for efficient deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes ' by Ziqi Zhang et al; Optics Letters 2024, 49(8), 2049.