III-V Epi contributes to QD PCSELs paper
UK firm III-V Epi has announced that its director of epitaxy, Neil Gerrard, is amongst the expert contributors to a white paper, 'Epitaxially regrown quantum dot photonic crystal surface emitting lasers', published earlier this year in Applied Physics Letters.
The team demonstrated quantum dot-based epitaxially regrown PCSELs (photonic crystal surface emitting lasers) at room temperature. The GaAs-based devices, which are monolithically integrated on the same wafer, exhibited ground state lasing at ∼1230 nm and excited state lasing at ∼1140 nm with threshold current densities of 0.69 and 1.05 kA/cm2, respectively. III-V Epi was responsible for the epitaxial regrowth of the devices.
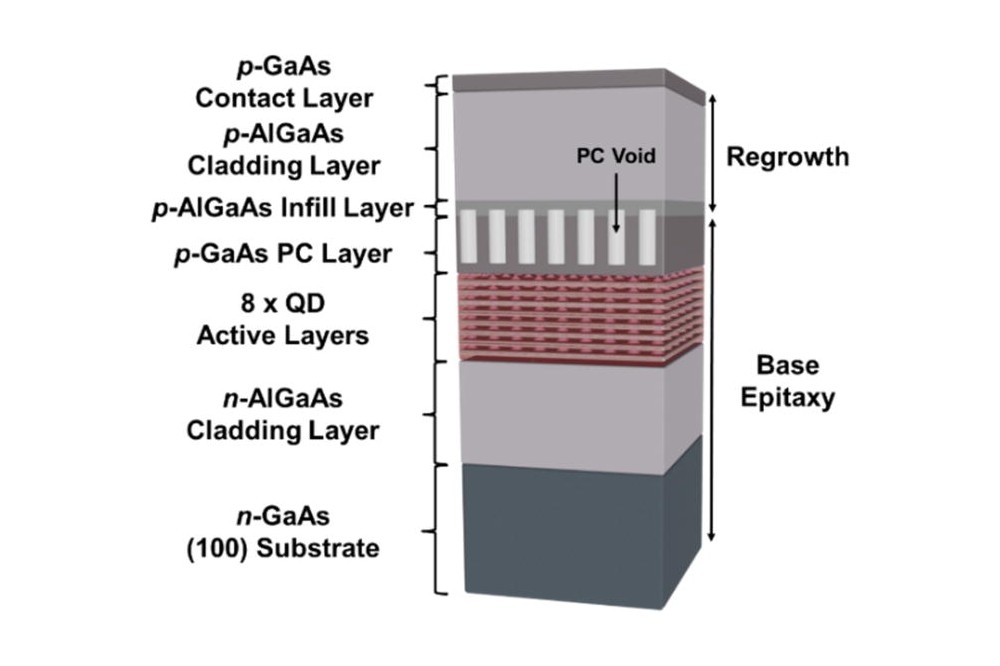
Pictured above is the schematic structure of the QD-PCSEL. The base epitaxy material, which includes eight layers of InAs QDs, was grown by MBE. The upper cladding layers, which encapsulate the PC layer, were regrown by MOVPE.
Gerrard said: “PCSELs are a new class of semiconductor laser which has a 2D photonic crystal within its device structure. They uniquely offer simultaneous high-power and single-mode vertical emission. They also offer features such as narrow divergence, beam steering, control of wavelength, and polarisation, making PCSELs attractive in a diverse range of semiconductor laser applications."
He added: “Epitaxial regrowth is the preferred method for fabricating PCSELs, as many detrimental defects associated with producing other types of lasers can be eliminated and high power and high efficiency realised. Epitaxial regrowth also brings greater flexibility in PC design, allowing for the build of both void-semiconductor contrast PCSELs, which offer the best performance in terms of power and efficiency, and all-semiconductor PCSELs, with large associated coupling coefficients.”