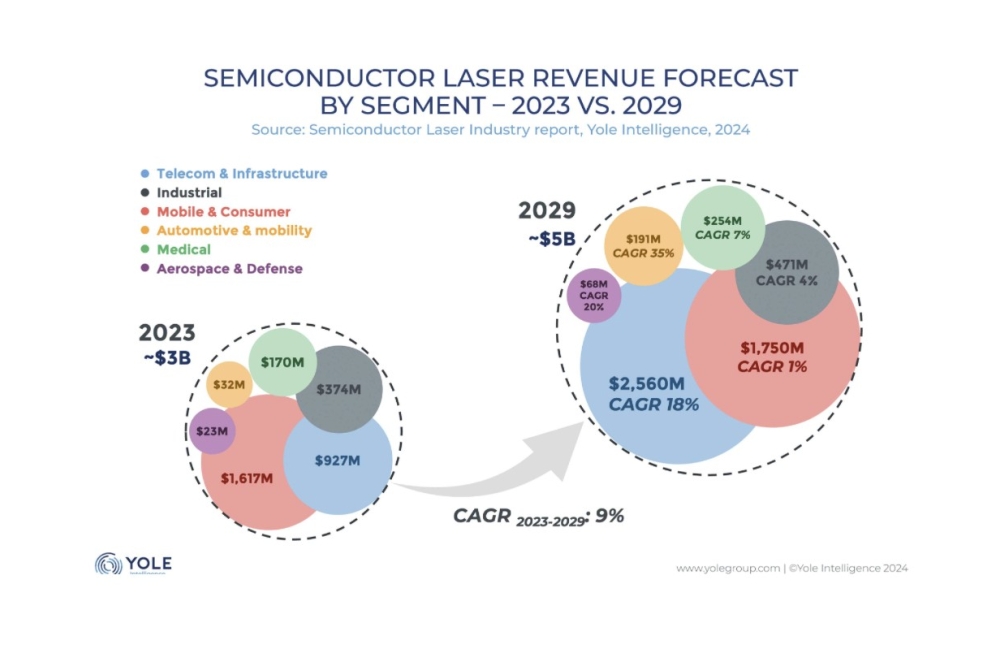
Technical Insight
NTT achieves 1 mW output from AlGaN-based UV-LED (Research Review)
Toshio Nishida and colleagues from NTT Basic Research Laboratories in Japan have reported an AlGaN-based SQW UV-LED with an output power of 1 mW. Room temperature CW operation gives a peak wavelength of 341343 nm (Appl. Phys.Lett. 2001 78(25) 3927). The device is grown by MOCVD on a SiC substrate. The backside contact is provided by a conductive AlGaN (18% Al) buffer layer with a short period (3 nm) alloy superlattice giving transparent and conducting p-side cladding. The active regions of the structures consist of 2 nm thick Al0.06Ga0.94N SQWs with Al0.12Ga0.88N barriers. Current confinement is provided by 20 nm thick n- and p-type Al0.3Ga0.7N layers below and above the SQW structure. The shows the I-L curves for three different LED structures tested under RT, CW operation: the inset shows the band structures of the devices. LED (b), which does not have carrier confinement layers, begins to show saturation at 100 mA injection current. Without confinement, carriers are spilling over from the SQW to the other side of the p-n junction. LEDs (a) and (c) are carrier-confined and show near linear characteristics up to 150 mA, though slope efficiency for LED (c) is lower than LED (a). This is ascribed to the optical reabsorption in the upper QWs. LED (a) did not show saturation until an injection current of 400 mA was reached. At this point, the output power was 1 mW. This output power is almost 10 times at half the injection current than that previously reported by this group.