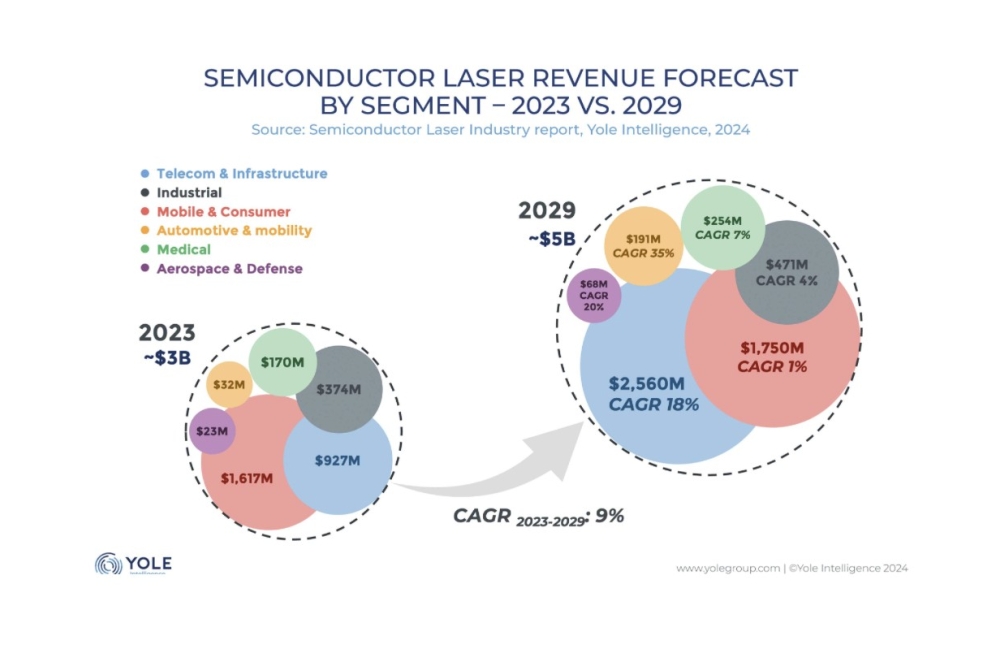
Technical Insight
Fiber-optic products (Asia News)
NTT has developed a 1550 nm VCSEL requiring a drive current of 0.38 mA, which is only 1% of the current required for typical 1550 nm edge-emitting lasers currently used in long-distance fiber communications. Together with the more efficient fiber coupling inherent to VCSELs, the lower power consumption promises to offer cost reductions in optical communications systems. NTT s device features a lower GaAs/AlGaAs mirror wafer-bonded to an InP-based active region, with an upper dielectric mirror. The low power consumption is achieved by the use of a semi-insulating InP layer to define the active region. This confines the current to the active region and provides a light guiding effect, increasing the power efficiency of the device. Increasing the levels of automation in fiber-optic component manufacturing is now recognized as crucial to lowering costs and improving uniformity and reliability. At present, fibers are often connected to components manually. Toshiba Machine Co has developed a device to automate fiber coupling by utilizing the control and alignment principles used in machine tools. The device positions the fibers in the placement grooves in components then welds them together using a laser. Nissei Sangyo has recently made an agreement with US company ADC to import and to sell ADC s products in Japan. The contract covers ADC s wavelength-tunable transmitters and 980 nm pump lasers. Nissei Sangyo hopes sales of these goods in Japan will reach 300 million ($2.5 million) in the first year and 2 billion ($17 million) by 2003. The Femtosecond Technology Research Association (FESTA), an organization of Japanese electronics companies including Toshiba, Fujitsu, Mitsubishi and NEC, has developed an ultra-fast semiconductor laser. Operating at the technologically important 1.5 m wavelength, the device has been pulsed at a frequency of 480 GHz. FESTA claims that by incorporating the laser into a WDM system, an effective frequency of 1 THz may be achievable.