French collaboration to focus on quantum photonics
Quandela, the CNRS, Université Paris-Saclay, and Université Paris Cité have announced a collaboration called QDlight Labcom focusing on research into quantum photonics and semiconductor single-photon source technology.
Over the course of six years, the teams will expand cooperation with a view to developing next generation quantum light emitters, as well as their applications in quantum information technology.
Quandela, a European photonic quantum computing firm, has produced and marketed quantum light emitters since 2017. These emitters, which consist of a quantum dot that behaves like an artificial atom in a semiconductor matrix, can generate a series of on-demand and indistinguishable single photons through a succession of laser pulses concentrating on this artificial atom.
In the optimal resonance and photon extraction conditions provided by the optical cavity in which it is positioned, these quantum dots can generate a photon flux with a rate of a few dozen megahertz, which efficiently implement quantum computing protocols on a photonic chip.
The new associated research laboratory aims to develop emitters and protocols to generate new quantum states of light, with a view to creating a fault-tolerant photonic quantum computer, and to demonstrating quantum communication protocols. A key part of the work will be focused on improving the quality of the quantum-dot-based photonic devices. This will notably involve growing materials of very high purity as well as increasing the reproducibility of photonic device production.
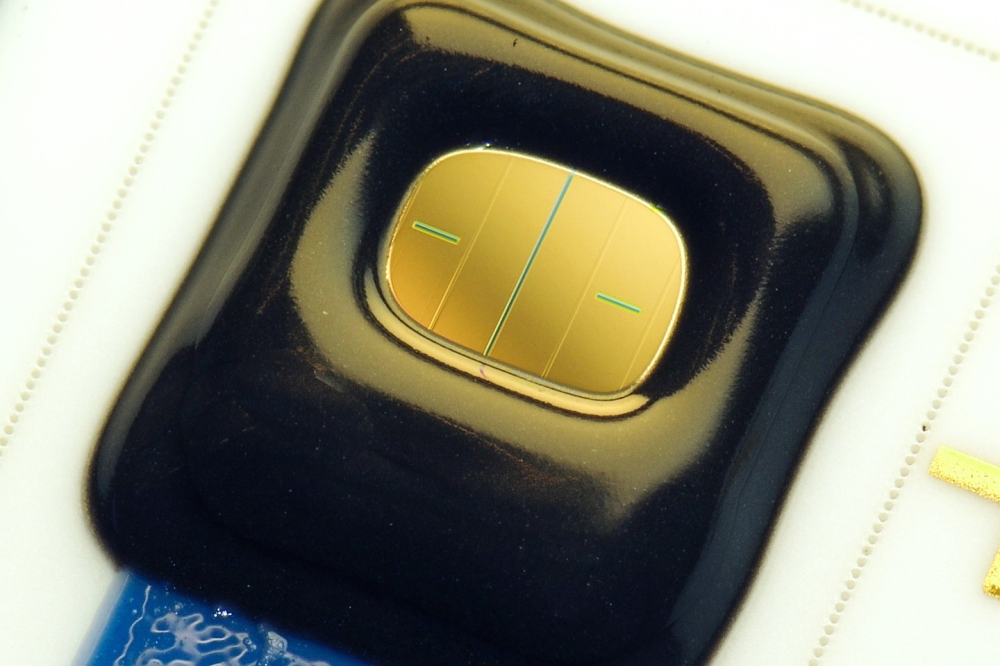
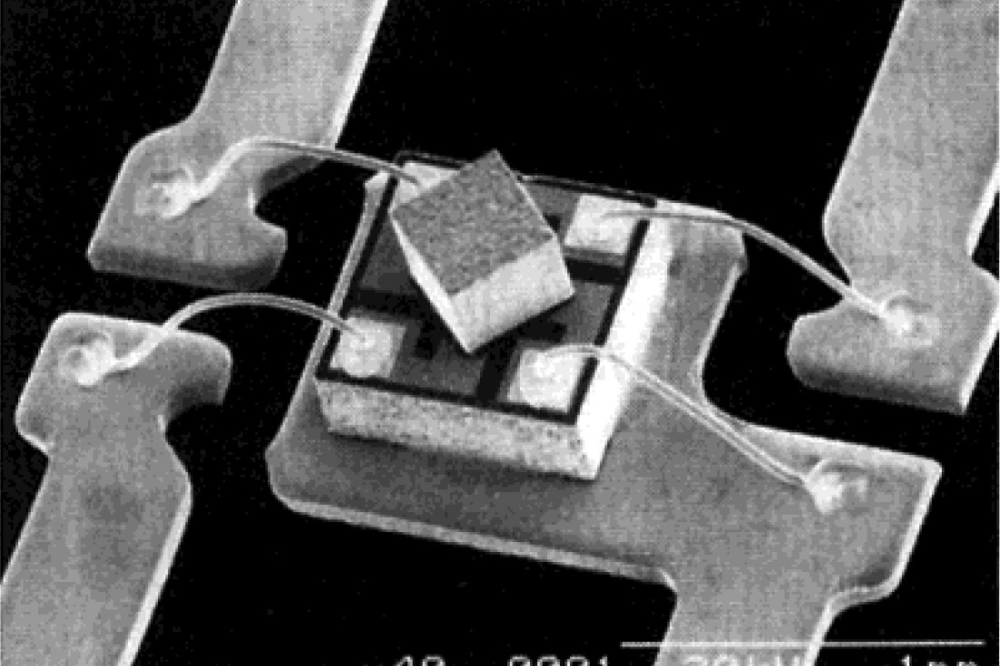
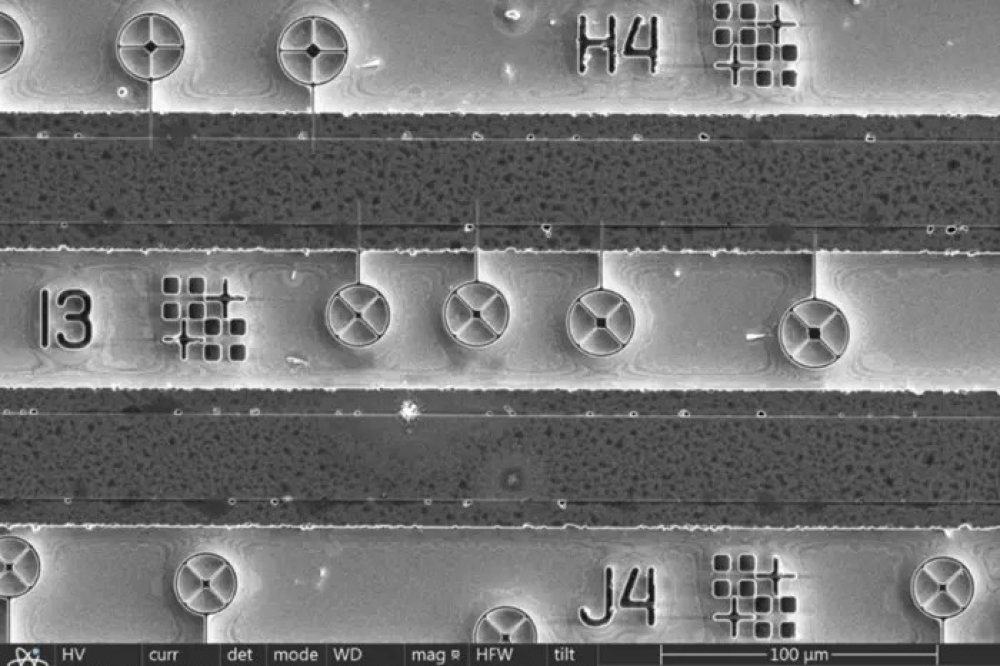
Pictured above: Scanning electron microscopy photograph showing the photonic devices produced by by engraving a precisely-centred cross pattern on each pre-selected quantum dot. Each of these patterns is connected to a metal line in order to apply grid voltage.