News Article
Sharp's solar cell has highest conversion efficiency of 37.9 percent
The firm managed to improve efficiency by incorporating an InGaAs layer at the bottom of its InGaP / GaAs compound solar cell
Sharp Corporation has achieved what it claims is the world's highest solar cell conversion efficiency of 37.9 percent.

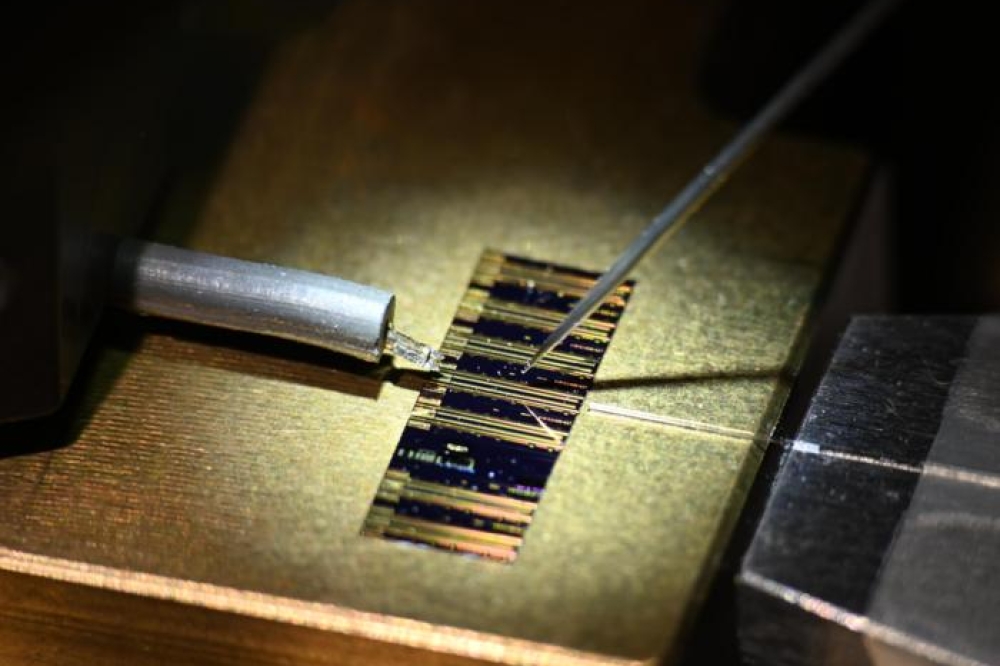
Sharp's 37.9 percent efficient III-V solar cell
This is based on a survey by Sharp as of April 24th, 2013, for non-concentrator solar cells at the research level.
The conversion efficiency was confirmed by the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST). This is one of several organisations that officially certifies energy conversion efficiency measurements in solar cells. The cell surface was approximately 1cm2.
Sharp achieved this latest breakthrough as a result of a research and development initiative promoted by Japan’s New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation (NEDO) on the theme of "R&D on Innovative Solar Cells."
NEDO is one of Japan's largest public management organisations for promoting research and development as well as for disseminating industrial, energy, and environmental technologies.
Compound solar cells utilise photo-absorption layers made from compounds consisting of two or more elements, such as indium and gallium. The basic structure of this latest triple-junction compound solar cell uses proprietary Sharp technology that enables efficient stacking of the three photo-absorption layers, with InGaAs as the bottom layer.
By optimising the relative proportions of indium, gallium, and arsenic, Sharp succeeded in increasing the efficiency with which the cell absorbs sunlight at its various wavelengths. This improvement enabled Sharp to achieve a solar cell conversion efficiency of 37.9 percent.
Sharp's aim for the future is to apply this latest development success to concentrator photovoltaic power systems that use lenses to collect and convert sunlight into electricity.
The company also foresees numerous other practical applications for the cells, such as on space satellites and vehicles.
Wavelength Distribution of Solar Photo-Energy and Wavelength Sensitivity of Triple-Junction Compound Solar Cell

Structure of Triple-Junction
Compound Solar Cell
・InGaP: Indium Gallium Phosphide
・GaAs: Gallium Arsenide
・InGaAs: Indium Gallium Arsenide
・Tunnel junction: Semiconductor junction where electricity flows as if through metal

Sharp's 37.9 percent efficient III-V solar cell
This is based on a survey by Sharp as of April 24th, 2013, for non-concentrator solar cells at the research level.
The conversion efficiency was confirmed by the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST). This is one of several organisations that officially certifies energy conversion efficiency measurements in solar cells. The cell surface was approximately 1cm2.
Sharp achieved this latest breakthrough as a result of a research and development initiative promoted by Japan’s New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation (NEDO) on the theme of "R&D on Innovative Solar Cells."
NEDO is one of Japan's largest public management organisations for promoting research and development as well as for disseminating industrial, energy, and environmental technologies.
Compound solar cells utilise photo-absorption layers made from compounds consisting of two or more elements, such as indium and gallium. The basic structure of this latest triple-junction compound solar cell uses proprietary Sharp technology that enables efficient stacking of the three photo-absorption layers, with InGaAs as the bottom layer.
By optimising the relative proportions of indium, gallium, and arsenic, Sharp succeeded in increasing the efficiency with which the cell absorbs sunlight at its various wavelengths. This improvement enabled Sharp to achieve a solar cell conversion efficiency of 37.9 percent.
Sharp's aim for the future is to apply this latest development success to concentrator photovoltaic power systems that use lenses to collect and convert sunlight into electricity.
The company also foresees numerous other practical applications for the cells, such as on space satellites and vehicles.
Wavelength Distribution of Solar Photo-Energy and Wavelength Sensitivity of Triple-Junction Compound Solar Cell

Structure of Triple-Junction
Compound Solar Cell
・InGaP: Indium Gallium Phosphide
・GaAs: Gallium Arsenide
・InGaAs: Indium Gallium Arsenide
・Tunnel junction: Semiconductor junction where electricity flows as if through metal